Generalized vector space model: Difference between revisions
en>Qwertyus m Category:Vector space model |
en>Kzhilton |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| class=wikitable align=right width=500 | |||
|- align=center | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t6.svg|120px]]<BR>[[7-orthoplex]]<BR>{{CDD|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node}} | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t5.svg|120px]]<BR>Rectified 7-orthoplex<BR>{{CDD|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node}} | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t4.svg|120px]]<BR>Birectified 7-orthoplex<BR>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node}} | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t3.svg|120px]]<BR>Trirectified 7-orthoplex<BR>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node}} | |||
|- align=center | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t2.svg|120px]]<BR>[[Birectified 7-cube]]<BR>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|4|node}} | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t1.svg|120px]]<BR>[[Rectified 7-cube]]<BR>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node_1|4|node}} | |||
|[[File:7-cube_t0.svg|120px]]<BR>[[7-cube]]<BR>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node_1}} | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=4|[[Orthogonal projection]]s in B<sub>7</sub> [[Coxeter plane]] | |||
|} | |||
In seven-dimensional [[geometry]], a '''rectified 7-orthoplex''' is a convex [[uniform 7-polytope]], being a [[Rectification (geometry)|rectification]] of the regular [[7-orthoplex]]. | |||
There are unique 7 degrees of rectifications, the zeroth being the [[7-orthoplex]], and the 6th and last being the [[7-cube]]. Vertices of the rectified 7-orthoplex are located at the edge-centers of the 7-orthoplex. Vertices of the birectified 7-orthoplex are located in the triangular face centers of the 7-orthoplex. Vertices of the trirectified 7-orthoplex are located in the [[tetrahedron|tetrahedral]] cell centers of the 7-orthoplex. | |||
== Rectified 7-orthoplex == | |||
{| class="wikitable" align="right" style="margin-left:10px" width="250" | |||
!bgcolor=#e7dcc3 colspan=2|Rectified 7-orthoplex | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Type||[[uniform 7-polytope]] | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Schläfli symbol]]|| r{3,3,3,3,3,4} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Coxeter-Dynkin diagram]]s||{{CDD|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|4|node}}<br>{{CDD|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node|split1|nodes}} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|6-faces||142 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|5-faces||1344 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|4-faces||3360 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Cells||3920 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Faces||2520 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Edges||840 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Vertices||84 | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Vertex figure]]||5-orthoplex prism | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Coxeter group]]s||C<sub>7</sub>, [3,3,3,3,3,4]<BR>D<sub>7</sub>, [3<sup>4,1,1</sup>] | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Properties||[[Convex polytope|convex]] | |||
|} | |||
The ''rectified 7-orthoplex'' is the [[vertex figure]] for the [[demihepteractic honeycomb]]. The rectified 7-orthoplex's 84 vertices represent the [[kissing number]] of a sphere-packing constructed from this honeycomb. | |||
:{{CDD|nodes_10ru|split2|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|split1|nodes}} or {{CDD|nodes_10ru|split2|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|3|node|4|node}} | |||
=== Alternate names=== | |||
* rectified heptacross | |||
* rectified hecatonicosoctaexon (Acronym rez) (Jonathan Bowers) - rectified 128-faceted polyexon<ref>Klitzing, (o3o3x3o3o3o4o - rez)</ref> | |||
=== Images === | |||
{{7-cube Coxeter plane graphs|t5|150}} | |||
=== Construction === | |||
There are two [[Coxeter group]]s associated with the ''rectified heptacross'', one with the C<sub>7</sub> or [4,3,3,3,3,3] Coxeter group, and a lower symmetry with two copies of pentacross facets, alternating, with the D<sub>7</sub> or [3<sup>4,1,1</sup>] Coxeter group. | |||
=== Cartesian coordinates === | |||
[[Cartesian coordinates]] for the vertices of a rectified heptacross, centered at the origin, edge length <math> \sqrt{2}\ </math> are all permutations of: | |||
: (±1,±1,0,0,0,0,0) | |||
==== Root vectors ==== | |||
Its 84 vertices represent the root vectors of the [[simple Lie group]] D<sub>7</sub>. The vertices can be seen in 3 [[hyperplane]]s, with the 21 vertices [[rectified 6-simplex]]s cells on opposite sides, and 42 vertices of an [[expanded 6-simplex]] passing through the center. When combined with the 14 vertices of the 7-orthoplex, these vertices represent the 98 root vectors of the B<sub>7</sub> and C<sub>7</sub> simple Lie groups. | |||
== Birectified 7-orthoplex == | |||
{| class="wikitable" align="right" style="margin-left:10px" width="250" | |||
!bgcolor=#e7dcc3 colspan=2|Birectified 7-orthoplex | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Type||[[uniform 7-polytope]] | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Schläfli symbol]]|| 2r{3,3,3,3,3,4} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Coxeter-Dynkin diagram]]s||{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|3|node|4|node}}<br>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|split1|nodes}} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|6-faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|5-faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|4-faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Cells|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Edges|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Vertices|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Vertex figure]]||{3}x{3,3,4} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Coxeter group]]s||C<sub>7</sub>, [3,3,3,3,3,4]<BR>D<sub>7</sub>, [3<sup>4,1,1</sup>] | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Properties||[[Convex polytope|convex]] | |||
|} | |||
=== Alternate names=== | |||
* Birectified heptacross | |||
* Birectified hecatonicosoctaexon (Acronym rez) (Jonathan Bowers) - birectified 128-faceted polyexon<ref>Klitzing, (o3o3x3o3o3o4o - barz)</ref> | |||
=== Images === | |||
{{7-cube Coxeter plane graphs|t4|150}} | |||
=== Cartesian coordinates === | |||
[[Cartesian coordinates]] for the vertices of a birectified 7-orthoplex, centered at the origin, edge length <math> \sqrt{2}\ </math> are all permutations of: | |||
: (±1,±1,±1,0,0,0,0) | |||
== Trirectified 7-orthoplex == | |||
{| class="wikitable" align="right" style="margin-left:10px" width="250" | |||
!bgcolor=#e7dcc3 colspan=2|Trirectified 7-orthoplex | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Type||[[uniform 7-polytope]] | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Schläfli symbol]]|| 3r{3,3,3,3,3,4} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Coxeter-Dynkin diagram]]s||{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|3|node|4|node}}<br>{{CDD|node|3|node|3|node|3|node_1|3|node|split1|nodes}} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|6-faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|5-faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|4-faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Cells|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Faces|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Edges|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Vertices|| | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Vertex figure]]||{3,3}x{3,4} | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|[[Coxeter group]]s||C<sub>7</sub>, [3,3,3,3,3,4]<BR>D<sub>7</sub>, [3<sup>4,1,1</sup>] | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor=#e7dcc3|Properties||[[Convex polytope|convex]] | |||
|} | |||
=== Alternate names=== | |||
* Trirectified heptacross | |||
* Trirectified hecatonicosoctaexon (trirectified 128-faceted polyexon) | |||
=== Images === | |||
{{7-cube Coxeter plane graphs|t3|150}} | |||
=== Cartesian coordinates === | |||
[[Cartesian coordinates]] for the vertices of a birectified 7-orthoplex, centered at the origin, edge length <math> \sqrt{2}\ </math> are all permutations of: | |||
: (±1,±1,±1,±1,0,0,0) | |||
== Notes== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
== References== | |||
* [[Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter|H.S.M. Coxeter]]: | |||
** H.S.M. Coxeter, ''Regular Polytopes'', 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973 | |||
** '''Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter''', editied by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [http://www.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0471010030.html] | |||
*** (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, ''Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I'', [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10] | |||
*** (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, ''Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II'', [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591] | |||
*** (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, ''Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III'', [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45] | |||
* [[Norman Johnson (mathematician)|Norman Johnson]] ''Uniform Polytopes'', Manuscript (1991) | |||
** N.W. Johnson: ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'', Ph.D. | |||
* {{KlitzingPolytopes|polyexa.htm|7D|uniform polytopes (polyexa)}} o3o3x3o3o3o4o - rez, o3o3x3o3o3o4o - barz | |||
== External links == | |||
*{{GlossaryForHyperspace | anchor=Cross | title=Cross polytope }} | |||
* [http://www.polytope.net/hedrondude/topes.htm Polytopes of Various Dimensions] | |||
* [http://tetraspace.alkaline.org/glossary.htm Multi-dimensional Glossary] | |||
{{polytopes}} | |||
[[Category:7-polytopes]] | |||
Revision as of 18:16, 14 January 2014
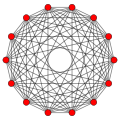 7-orthoplex Template:CDD |
 Rectified 7-orthoplex Template:CDD |
 Birectified 7-orthoplex Template:CDD |
 Trirectified 7-orthoplex Template:CDD |
 Birectified 7-cube Template:CDD |
 Rectified 7-cube Template:CDD |
 7-cube Template:CDD | |
| Orthogonal projections in B7 Coxeter plane | |||
|---|---|---|---|
In seven-dimensional geometry, a rectified 7-orthoplex is a convex uniform 7-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 7-orthoplex.
There are unique 7 degrees of rectifications, the zeroth being the 7-orthoplex, and the 6th and last being the 7-cube. Vertices of the rectified 7-orthoplex are located at the edge-centers of the 7-orthoplex. Vertices of the birectified 7-orthoplex are located in the triangular face centers of the 7-orthoplex. Vertices of the trirectified 7-orthoplex are located in the tetrahedral cell centers of the 7-orthoplex.
Rectified 7-orthoplex
| Rectified 7-orthoplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 7-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | r{3,3,3,3,3,4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | Template:CDD Template:CDD |
| 6-faces | 142 |
| 5-faces | 1344 |
| 4-faces | 3360 |
| Cells | 3920 |
| Faces | 2520 |
| Edges | 840 |
| Vertices | 84 |
| Vertex figure | 5-orthoplex prism |
| Coxeter groups | C7, [3,3,3,3,3,4] D7, [34,1,1] |
| Properties | convex |
The rectified 7-orthoplex is the vertex figure for the demihepteractic honeycomb. The rectified 7-orthoplex's 84 vertices represent the kissing number of a sphere-packing constructed from this honeycomb.
Alternate names
- rectified heptacross
- rectified hecatonicosoctaexon (Acronym rez) (Jonathan Bowers) - rectified 128-faceted polyexon[1]
Images
Template:7-cube Coxeter plane graphs
Construction
There are two Coxeter groups associated with the rectified heptacross, one with the C7 or [4,3,3,3,3,3] Coxeter group, and a lower symmetry with two copies of pentacross facets, alternating, with the D7 or [34,1,1] Coxeter group.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a rectified heptacross, centered at the origin, edge length are all permutations of:
- (±1,±1,0,0,0,0,0)
Root vectors
Its 84 vertices represent the root vectors of the simple Lie group D7. The vertices can be seen in 3 hyperplanes, with the 21 vertices rectified 6-simplexs cells on opposite sides, and 42 vertices of an expanded 6-simplex passing through the center. When combined with the 14 vertices of the 7-orthoplex, these vertices represent the 98 root vectors of the B7 and C7 simple Lie groups.
Birectified 7-orthoplex
| Birectified 7-orthoplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 7-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | 2r{3,3,3,3,3,4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | Template:CDD Template:CDD |
| 6-faces | |
| 5-faces | |
| 4-faces | |
| Cells | |
| Faces | |
| Edges | |
| Vertices | |
| Vertex figure | {3}x{3,3,4} |
| Coxeter groups | C7, [3,3,3,3,3,4] D7, [34,1,1] |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
- Birectified heptacross
- Birectified hecatonicosoctaexon (Acronym rez) (Jonathan Bowers) - birectified 128-faceted polyexon[2]
Images
Template:7-cube Coxeter plane graphs
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a birectified 7-orthoplex, centered at the origin, edge length are all permutations of:
- (±1,±1,±1,0,0,0,0)
Trirectified 7-orthoplex
| Trirectified 7-orthoplex | |
|---|---|
| Type | uniform 7-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | 3r{3,3,3,3,3,4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | Template:CDD Template:CDD |
| 6-faces | |
| 5-faces | |
| 4-faces | |
| Cells | |
| Faces | |
| Edges | |
| Vertices | |
| Vertex figure | {3,3}x{3,4} |
| Coxeter groups | C7, [3,3,3,3,3,4] D7, [34,1,1] |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
- Trirectified heptacross
- Trirectified hecatonicosoctaexon (trirectified 128-faceted polyexon)
Images
Template:7-cube Coxeter plane graphs
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a birectified 7-orthoplex, centered at the origin, edge length are all permutations of:
- (±1,±1,±1,±1,0,0,0)
Notes
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
References
- H.S.M. Coxeter:
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, editied by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [1]
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10]
- (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II, [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D.
- Template:KlitzingPolytopes o3o3x3o3o3o4o - rez, o3o3x3o3o3o4o - barz
