Neutrino decoupling
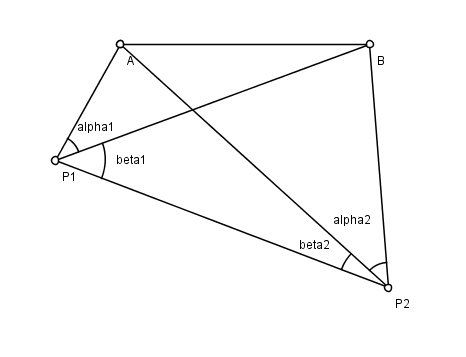
Hansen's problem is a problem in planar surveying, named after the astronomer Peter Andreas Hansen (1795–1874), who worked on the geodetic survey of Denmark. There are two known points A and B, and two unknown points P1 and P2. From P1 and P2 an observer measures the angles made by the lines of sight to each of the other three points. The problem is to find the positions of P1 and P2. See figure; the angles measured are (α1, β1, α2, β2).
Since it involves observations of angles made at unknown points, the problem is an example of resection (as opposed to intersection).
Solution method overview
Define the following angles: γ = P1AP2, δ = P1BP2, φ = P2AB, ψ = P1BA. As a first step we will solve for φ and ψ. The sum of these two unknown angles is equal to the sum of β1 and β2, yielding the following equation:
A second equation can be found more laboriously, as follows. The law of sines yields
combining these together we get
An entirely analogous reasoning on the other side yields
Setting these two equal gives
Using a known trigonometric identity this ratio of sines can be expressed as the tangent of an angle difference:
This is the second equation we need. Once we solve the two equations for the two unknowns and , we can use either of the two expressions above for to find P1P2 since AB is known. We can then find all the other segments using the law of sines.[1]
Solution algorithm
We are given four angles (α1, β1, α2, β2) and the distance AB. The calculation proceeds as follows:
- Calculate
- or equivalently,
- If one of these fractions has a denominator close to zero, use the other one.
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.