Ant on a rubber rope
In kinematics, cognate linkages are linkages that ensure the same input-output relationship or coupler curve geometry, while being dimensionally dissimilar. In case of four-bar linkage coupler cognates, the Roberts–Chebyschev Theorem, after Samuel Roberts and Pafnuty Chebyshev,[1] states that each coupler curve can be generated by three different four-bar linkages. These four-bar linkages can be constructed using similar triangles and parallelograms, and the Cayley diagram (named after Arthur Cayley).
Overconstrained mechanisms can be obtained by connecting two or more cognate linkages together.
Roberts–Chebyschev theorem
The theorem states for a given coupler-curve there exist three four-bar linkages, three geared five-bar linkages, and more six-bar linkages which will generate the same path. The method for generating the additional two the four bar linkages from a single four-bar mechanism is described below, using the Cayley diagram.
How to construct path cognate linkages
Cayley diagram
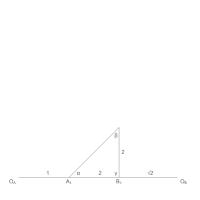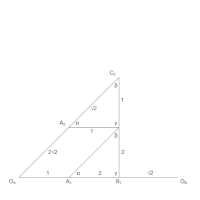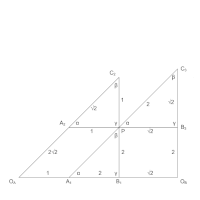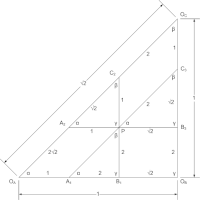
From original triangle, ΔA1,D,B1
- Sketch Cayley diagram
- Using parallelograms, find A2 and B3 //OA,A1,D,A2 and //OB,B1,D,B3
- Using similar triangles, find C2 and C3 ΔA2,C2,D and ΔD,C3,B3
- Using a parallelogram, find OC //OC,C2,D,C3
- Check similar triangles ΔOA,OC,OB
- Separate left and right cognate
- Put dimensions on Cayley diagram
Dimensional relationships

The lengths of the four members can be found by using the law of sines. Both KL and KR are found as follows.
| Linkage | Ground | Crank 1 | Crank 2 | Coupler |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
| Left cognate | KLR1 | KLR3 | KLR4 | KLR2 |
| Right cognate | KRR1 | KRR3 | KRR4 | KRR2 |
Conclusions
- If and only if the original is a Class I chain Both 4-bar cognates will be class I chains.
- If the original is a drag-link (double crank), both cognates will be drag links.
- If the original is a crank-rocker, one cognate will be a crank-rocker, and the second will be a double-rocker.
- If the original is a double-rocker, the cognates will be crank-rockers.
See also
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
- 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - Samuel Roberts (1876) "On Three-bar Motion in Plane Space", Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society, vol 7.
- Hartenberg, R.S. & J. Denavit (1964) Kinematic synthesis of linkages, p 169, New York: McGraw-Hill, weblink from Cornell University.
External links
- Four- and six-bar function cognates and overconstrained mechanisms
- Applications of Watt II function generator cognates
- Coupler cognate mechanisms of certain parallelogram forms of Watt's six-link mechanism
- ↑ Roberts and Chebyshev (Springer) Retrieved 2012-10-12


