Main Page: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{other uses}} | |||
''' | {{redirect|Jostle|the racehorse|Jostle (horse)}} | ||
A '''collision''' is an isolated event in which two or more moving bodies (colliding bodies) exert forces on each other for a relatively short time. | |||
A collision is not constrained to only referring to moving bodies it can also refer to electronic transactions which share a common resource such as a bus interface. In this case a collision refers to two simultaneous requests for the shared resource being made. | |||
Although the most common colloquial use of the word "collision" refers to [[accident]]s in which two or more objects collide, the scientific use of the word "collision" implies nothing about the magnitude of the forces. | |||
: | Some examples of physical interactions that scientists would consider collisions: | ||
* An insect touches its antenna to the leaf of a plant. The antenna is said to collide with leaf. | |||
* A cat walks delicately through the grass. Each contact that its paws make with the ground is a collision. Each brush of its fur against a blade of grass is a collision. | |||
Some colloquial uses of the word collision are: | |||
* [[automobile collision]], two cars colliding | |||
* [[mid-air collision]], two planes colliding | |||
* [[ship collision]], two ships colliding | |||
==Overview== | |||
[[File:Deflection.png|right|thumb|250px|[[Deflection (physics)|Deflection]] happens when an object hits a plane surface. If the kinetic energy after impact is the same as before impact, it is an elastic collision. If kinetic energy is lost, it is an inelastic collision. It is not possible to determine from the diagram whether the illustrated collision was elastic or inelastic, because no velocities are provided. The most one can say is that the collision was not perfectly-inelastic, because in that case the ball would have stuck to the wall.]] | |||
Collision is short duration interaction between two bodies or more than two bodies simultaneously causeng change in motion of bodies involved due to internal forces acted between them during this . Collisions involve forces (there is a change in [[velocity]]). The magnitude of the velocity difference at impact is called the closing speed. All collisions conserve [[momentum]]. What distinguishes different types of collisions is whether they also conserve [[kinetic energy]].Line of impact - It is the line which is common normal for surfaces are closest or in contact during impact. This is the line along which internal force of collision acts during impact and Newton's coefficient of restitution is defined only along this line. | |||
Specifically, collisions can either be ''[[elastic collision|elastic]],'' meaning they conserve both momentum and kinetic energy, or ''[[inelastic collision|inelastic]],'' meaning they conserve momentum but not kinetic energy. An inelastic collision is sometimes also called a ''plastic collision.'' | |||
A “perfectly-inelastic” collision (also called a "perfectly-plastic" collision) is a limiting case of inelastic collision in which the two bodies stick together after impact. | |||
The degree to which a collision is elastic or inelastic is quantified by the [[coefficient of restitution]], a value that generally ranges between zero and one. A perfectly elastic collision has a coefficient of restitution of one; a perfectly-inelastic collision has a coefficient of restitution of zero. | |||
one | ==Types of collisions== | ||
There are two types of collision between two bodies- 1)head on collision or one dimensional collision - where nelocity of each just before impact is not alon line of impact. 2)non head on collision or oblique collision or two dimensional collision- where velocity of each is not long line of impact just before collision. | |||
: | Though there are two special case of any collision as written below according to coefficient of restitution : | ||
1)A perfectly [[elastic collision]] is defined as one in which there is no loss of [[kinetic energy]] in the collision. In reality, any macroscopic collision between objects will convert some kinetic energy to [[internal energy]] and other forms of energy, so no large scale impacts are perfectly elastic. However, some problems are sufficiently close to perfectly elastic that they can be approximated as such.Here coefficient of restitution is one. | |||
2)An [[inelastic collision]] is one in which part of the kinetic energy is changed to some other form of energy in the collision. [[Momentum]] is conserved in inelastic collisions (as it is for elastic collisions), but one cannot track the kinetic energy through the collision since some of it is converted to other forms of energy.Here coefficient of restitution is not one. | |||
In any type of collision there is a phase when for a moment colliding bodies have same velocity along line of impact then kinetic energy of bodies reduces to its minimum during this phase and may be called as maximum deformation phase for which momentarily coefficient of restitution become one. | |||
Collisions in [[ideal gases]] approach perfectly elastic collisions, as do scattering interactions of [[sub-atomic particles]] which are deflected by the [[electromagnetic force]]. Some large-scale interactions like the slingshot type gravitational interactions between satellites and planets are perfectly elastic. | |||
Collisions between hard spheres may be nearly elastic, so it is useful to calculate the limiting case of an elastic collision. The assumption of conservation of momentum as well as the conservation of kinetic energy makes possible the calculation of the final velocities in two-body collisions. | |||
==Analytical vs. numerical approaches towards resolving collisions == | |||
Relatively few problems involving collisions can be solved analytically; the remainder require [[numerical methods]]. An important problem in simulating collisions is determining whether two objects have in fact collided. This problem is called [[collision detection]]. | |||
{{cleanup|section|date=February 2011}}. | |||
== | == Examples of collisions that can be solved analytically == | ||
===Billiards=== | |||
{{Anchor|Cue sports}}Collisions play an important role in [[cue sports]]. Because the collisions between [[billiard balls]] are nearly elastic, and the balls roll on a surface that produces low [[rolling friction]], their behavior is often used to illustrate [[Newton's laws of motion]]. After a zero-friction collision of a moving ball with a stationary one of equal mass, the angle between the directions of the two balls is 90 degrees. This is an important fact that professional billiards players take into account,<ref>{{cite web|last=Alciatore |first=David G. |date=January 2006 |url=http://billiards.colostate.edu/technical_proofs/TP_3-1.pdf |title=TP 3.1 90° rule |format=PDF |accessdate=2008-03-08 }}</ref> although it assumes the ball is moving frictionlessly across the table rather than rolling with friction. | |||
Consider an elastic collision in 2 dimensions of any 2 masses m<sub>1</sub> and m<sub>2</sub>, with respective initial velocities '''u<sub>1</sub>''' and '''u<sub>2</sub>''' = '''0''', and final velocities '''V<sub>1</sub>''' and '''V<sub>2</sub>'''. | |||
Conservation of momentum gives m<sub>1</sub>'''u'''<sub>1</sub> = m<sub>1'''</sub>V<sub>1</sub>'''+ m<sub>2'''</sub>V<sub>2'''</sub>. | |||
Conservation of energy for an elastic collision gives (1/2)m<sub>1</sub>|'''u<sub>1</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup> = (1/2)m<sub>1</sub>|'''V<sub>1</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup> + (1/2)m<sub>2</sub>|'''V<sub>2</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup>. | |||
Now consider the case m<sub>1</sub> = m<sub>2</sub>: we obtain '''u<sub>1</sub>'''='''V<sub>1</sub>'''+'''V<sub>2</sub>''' and |'''u<sub>1</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup> = |'''V<sub>1</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup>+|'''V<sub>2</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup>. | |||
Taking the [[dot product]] of each side of the former equation with itself, |'''u<sub>1</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup> = '''u<sub>1</sub>•u<sub>1</sub>''' = |'''V<sub>1</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup>+|'''V<sub>2</sub>'''|<sup>2</sup>+2'''V<sub>1</sub>•V<sub>2</sub>'''. Comparing this with the latter equation gives '''V<sub>1</sub>•V<sub>2</sub>''' = 0, so they are perpendicular unless '''V<sub>1</sub>''' is the zero vector (which occurs if and only if the collision is head-on). | |||
===Perfectly inelastic collision=== | |||
[[Image:Inelastischer stoß.gif|a completely inelastic collision between equal masses]] | |||
In a perfectly inelastic collision, i.e., a zero [[coefficient of restitution]], the colliding particles stick together. It is necessary to consider conservation of momentum: | |||
::<math>m_a \mathbf u_a + m_b \mathbf u_b = \left( m_a + m_b \right) \mathbf v \,</math> | |||
where '''v''' is the final velocity, which is hence given by | |||
::<math>\mathbf v=\frac{m_a \mathbf u_a + m_b \mathbf u_b}{m_a + m_b}</math> | |||
The reduction of total kinetic energy is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision in a [[center of momentum frame]] with respect to the system of two particles, because in such a frame the kinetic energy after the collision is zero. In this frame most of the kinetic energy before the collision is that of the particle with the smaller mass. In another frame, in addition to the reduction of kinetic energy there may be a transfer of kinetic energy from one particle to the other; the fact that this depends on the frame shows how relative this is. | |||
With time reversed we have the situation of two objects pushed away from each other, e.g. shooting a [[projectile]], or a [[rocket]] applying [[thrust]] (compare the [[Tsiolkovsky rocket equation#Derivation|derivation of the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation]]). | |||
== Examples of collisions analyzed numerically== | |||
===Animal locomotion=== | |||
Collisions of an animal's foot or paw with the underlying substrate are generally termed ground reaction forces. These collisions are inelastic, as kinetic energy is not conserved. An important research topic in [[prosthetics]] is quantifying the forces generated during the foot-ground collisions associated with both disabled and non-disabled gait. This quantification typically requires subjects to walk across a [[force platform]] (sometimes called a "force plate") as well as detailed [[kinematic]] and [[Dynamics (mechanics)|dynamic]] (sometimes termed kinetic) analysis. | |||
== | == Collisions used as a experimental tool == | ||
Collisions can be used as an experimental technique to study material properties of objects and other physical phenomena. | |||
== See also == | === Space exploration=== | ||
* [[ | An object may deliberately be made to crash-land on another celestial body, to do measurements and send them to Earth before being destroyed, or to allow instruments elsewhere to observe the effect. See e.g.: | ||
*During [[Apollo 13]], [[Apollo 14]], [[Apollo 15]], [[Apollo 16]] and [[Apollo 17]], the [[S-IVB]] (the rocket's third stage) was crashed into the [[Moon]] in order to perform seismic measurement used for characterizing the lunar core. | |||
* [[Deep Impact (spacecraft)|''Deep Impact'']] | |||
* [[SMART-1]] - [[European Space Agency]] satellite | |||
* [[Moon impact probe]] - [[ISRO]] probe | |||
=== Mathematical description of molecular collisions === | |||
Let the linear, angular and internal momenta of a molecule be given by the set of ''r'' variables { ''p''<sub>i</sub> }. The state of a molecule may then be described by the range ''δw''<sub>i</sub> = δ''p''<sub>1</sub>δ''p''<sub>2</sub>δ''p''<sub>3</sub> ... δ''p''<sub>r</sub>. There are many such ranges corresponding to different states; a specific state may be denoted by the index ''i''. Two molecules undergoing a collision can thus be denoted by (''i'', ''j'') (Such an ordered pair is sometimes known as a ''constellation''.) | |||
It is convenient to suppose that two molecules exert a negligible effect on each other unless their centre of gravities approach within a critical distance ''b''. A collision therefore begins when the respective centres of gravity arrive at this critical distance, and is completed when they again reach this critical distance on their way apart. Under this model, a collision is completely described by the matrix <math>\begin{pmatrix}i&j\\k&l\end{pmatrix} </math>, which refers to the constellation (''i'', ''j'') before the collision, and the (in general different) constellation (''k'', ''l'') after the collision. | |||
This notation is convenient in proving Boltzmann's [[H-theorem]] of [[statistical mechanics]]. | |||
==Attack by means of a deliberate collision== | |||
Types of attack by means of a deliberate collision include: | |||
* with the body: unarmed [[Strike (attack)|striking]], [[Punch (strike)|punching]], [[kick]]ing, [[martial arts]], [[pugilism]] | |||
* striking directly with a weapon, such as a [[sword]], [[club (weapon)|club]] or [[axe]] | |||
* [[ramming]] with an object or vehicle, e.g.: | |||
** a car deliberately crashing into a building to break into it | |||
** a [[battering ram]], medieval weapon used for breaking down large doors, also a modern version is used by police forces during raids | |||
An attacking collision with a distant object can be achieved by throwing or launching a [[projectile]]. | |||
==See also== | |||
{{multicol}} | |||
*[[Ballistic pendulum]] | |||
*[[Coefficient of restitution]] | |||
*[[Collision detection]] | |||
*[[Collision (telecommunications)]] | |||
*[[Car accident]] | |||
*[[Elastic collision]] | |||
*[[Friction]] | |||
* [[Head-on collision]] | |||
*[[Impact crater]] | |||
{{multicol-break}} | |||
*[[Impact event]] | |||
*[[Inelastic collision]] | |||
*[[Kinetic theory]]<br /> - collisions between [[molecule]]s | |||
*[[Mid-air collision]] | |||
*[[Projectile]] | |||
*[[Space debris]] | |||
* [[Train wreck]] | |||
{{multicol-end}} | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
{{reflist|1}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
* | * {{cite book | author=Tolman, R. C. | title=The Principles of Statistical Mechanics | publisher=Clarendon Press | year=1938 | location=Oxford}} Reissued (1979) New York: Dover ISBN 0-486-63896-0. | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
*[http:// | *[http://www.regispetit.com/bil_praa.htm Three Dimensional Collision] - Oblique inelastic collision between two homogeneous spheres. | ||
*[http://www. | *[http://www.publicliterature.org/tools/collisions/ Two Dimensional Collision] - Java applet that simulates elastic collisions. | ||
*[http://www.physics-lab.net/applets/one-dimensional-collisions One Dimensional Collision] - One Dimensional Collision Flash Applet. | |||
*[http://www.physics-lab.net/applets/two-dimensional-collisions Two Dimensional Collision] - Two Dimensional Collision Flash Applet. | |||
[[Category:Mechanics]] | |||
[[Category:Introductory physics]] | |||
[[ar:تصادم]] | |||
[[ | [[cs:Ráz těles]] | ||
[[ | [[da:Kollision]] | ||
[[ | [[de:Stoß (Physik)]] | ||
[[ | [[fa:برخورد]] | ||
[[fr:Collision]] | |||
[[ko:충돌]] | |||
[[it:Urto]] | |||
[[lt:Smūgis]] | |||
[[hu:Ütközés]] | |||
[[nl:Botsing (natuurkunde)]] | |||
[[ja:衝突]] | |||
[[pl:Zderzenie]] | |||
[[pt:Colisão]] | |||
[[ro:Coliziune]] | |||
[[ru:Удар]] | |||
[[simple:Collision]] | |||
[[sl:Trk]] | |||
[[sv:Stöt (mekanik)]] | |||
[[zh:碰撞]] | |||
Revision as of 09:30, 9 August 2014
I'm Fernando (21) from Seltjarnarnes, Iceland.
I'm learning Norwegian literature at a local college and I'm just about to graduate.
I have a part time job in a the office.
my site; wellness [continue reading this..]
Name: Jodi Junker
My age: 32
Country: Netherlands
Home town: Oudkarspel
Post code: 1724 Xg
Street: Waterlelie 22
my page - www.hostgator1centcoupon.info
A collision is an isolated event in which two or more moving bodies (colliding bodies) exert forces on each other for a relatively short time.
A collision is not constrained to only referring to moving bodies it can also refer to electronic transactions which share a common resource such as a bus interface. In this case a collision refers to two simultaneous requests for the shared resource being made.
Although the most common colloquial use of the word "collision" refers to accidents in which two or more objects collide, the scientific use of the word "collision" implies nothing about the magnitude of the forces.
Some examples of physical interactions that scientists would consider collisions:
- An insect touches its antenna to the leaf of a plant. The antenna is said to collide with leaf.
- A cat walks delicately through the grass. Each contact that its paws make with the ground is a collision. Each brush of its fur against a blade of grass is a collision.
Some colloquial uses of the word collision are:
- automobile collision, two cars colliding
- mid-air collision, two planes colliding
- ship collision, two ships colliding
Overview
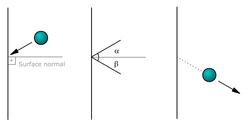
Collision is short duration interaction between two bodies or more than two bodies simultaneously causeng change in motion of bodies involved due to internal forces acted between them during this . Collisions involve forces (there is a change in velocity). The magnitude of the velocity difference at impact is called the closing speed. All collisions conserve momentum. What distinguishes different types of collisions is whether they also conserve kinetic energy.Line of impact - It is the line which is common normal for surfaces are closest or in contact during impact. This is the line along which internal force of collision acts during impact and Newton's coefficient of restitution is defined only along this line.
Specifically, collisions can either be elastic, meaning they conserve both momentum and kinetic energy, or inelastic, meaning they conserve momentum but not kinetic energy. An inelastic collision is sometimes also called a plastic collision.
A “perfectly-inelastic” collision (also called a "perfectly-plastic" collision) is a limiting case of inelastic collision in which the two bodies stick together after impact.
The degree to which a collision is elastic or inelastic is quantified by the coefficient of restitution, a value that generally ranges between zero and one. A perfectly elastic collision has a coefficient of restitution of one; a perfectly-inelastic collision has a coefficient of restitution of zero.
Types of collisions
There are two types of collision between two bodies- 1)head on collision or one dimensional collision - where nelocity of each just before impact is not alon line of impact. 2)non head on collision or oblique collision or two dimensional collision- where velocity of each is not long line of impact just before collision.
Though there are two special case of any collision as written below according to coefficient of restitution :
1)A perfectly elastic collision is defined as one in which there is no loss of kinetic energy in the collision. In reality, any macroscopic collision between objects will convert some kinetic energy to internal energy and other forms of energy, so no large scale impacts are perfectly elastic. However, some problems are sufficiently close to perfectly elastic that they can be approximated as such.Here coefficient of restitution is one.
2)An inelastic collision is one in which part of the kinetic energy is changed to some other form of energy in the collision. Momentum is conserved in inelastic collisions (as it is for elastic collisions), but one cannot track the kinetic energy through the collision since some of it is converted to other forms of energy.Here coefficient of restitution is not one. In any type of collision there is a phase when for a moment colliding bodies have same velocity along line of impact then kinetic energy of bodies reduces to its minimum during this phase and may be called as maximum deformation phase for which momentarily coefficient of restitution become one.
Collisions in ideal gases approach perfectly elastic collisions, as do scattering interactions of sub-atomic particles which are deflected by the electromagnetic force. Some large-scale interactions like the slingshot type gravitational interactions between satellites and planets are perfectly elastic.
Collisions between hard spheres may be nearly elastic, so it is useful to calculate the limiting case of an elastic collision. The assumption of conservation of momentum as well as the conservation of kinetic energy makes possible the calculation of the final velocities in two-body collisions.
Analytical vs. numerical approaches towards resolving collisions
Relatively few problems involving collisions can be solved analytically; the remainder require numerical methods. An important problem in simulating collisions is determining whether two objects have in fact collided. This problem is called collision detection.
Examples of collisions that can be solved analytically
Billiards
<Cue sports>...</Cue sports>Collisions play an important role in cue sports. Because the collisions between billiard balls are nearly elastic, and the balls roll on a surface that produces low rolling friction, their behavior is often used to illustrate Newton's laws of motion. After a zero-friction collision of a moving ball with a stationary one of equal mass, the angle between the directions of the two balls is 90 degrees. This is an important fact that professional billiards players take into account,[1] although it assumes the ball is moving frictionlessly across the table rather than rolling with friction.
Consider an elastic collision in 2 dimensions of any 2 masses m1 and m2, with respective initial velocities u1 and u2 = 0, and final velocities V1 and V2.
Conservation of momentum gives m1u1 = m1V1+ m2V2.
Conservation of energy for an elastic collision gives (1/2)m1|u1|2 = (1/2)m1|V1|2 + (1/2)m2|V2|2.
Now consider the case m1 = m2: we obtain u1=V1+V2 and |u1|2 = |V1|2+|V2|2.
Taking the dot product of each side of the former equation with itself, |u1|2 = u1•u1 = |V1|2+|V2|2+2V1•V2. Comparing this with the latter equation gives V1•V2 = 0, so they are perpendicular unless V1 is the zero vector (which occurs if and only if the collision is head-on).
Perfectly inelastic collision
In a perfectly inelastic collision, i.e., a zero coefficient of restitution, the colliding particles stick together. It is necessary to consider conservation of momentum:
where v is the final velocity, which is hence given by
The reduction of total kinetic energy is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision in a center of momentum frame with respect to the system of two particles, because in such a frame the kinetic energy after the collision is zero. In this frame most of the kinetic energy before the collision is that of the particle with the smaller mass. In another frame, in addition to the reduction of kinetic energy there may be a transfer of kinetic energy from one particle to the other; the fact that this depends on the frame shows how relative this is. With time reversed we have the situation of two objects pushed away from each other, e.g. shooting a projectile, or a rocket applying thrust (compare the derivation of the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation).
Examples of collisions analyzed numerically
Animal locomotion
Collisions of an animal's foot or paw with the underlying substrate are generally termed ground reaction forces. These collisions are inelastic, as kinetic energy is not conserved. An important research topic in prosthetics is quantifying the forces generated during the foot-ground collisions associated with both disabled and non-disabled gait. This quantification typically requires subjects to walk across a force platform (sometimes called a "force plate") as well as detailed kinematic and dynamic (sometimes termed kinetic) analysis.
Collisions used as a experimental tool
Collisions can be used as an experimental technique to study material properties of objects and other physical phenomena.
Space exploration
An object may deliberately be made to crash-land on another celestial body, to do measurements and send them to Earth before being destroyed, or to allow instruments elsewhere to observe the effect. See e.g.:
- During Apollo 13, Apollo 14, Apollo 15, Apollo 16 and Apollo 17, the S-IVB (the rocket's third stage) was crashed into the Moon in order to perform seismic measurement used for characterizing the lunar core.
- Deep Impact
- SMART-1 - European Space Agency satellite
- Moon impact probe - ISRO probe
Mathematical description of molecular collisions
Let the linear, angular and internal momenta of a molecule be given by the set of r variables { pi }. The state of a molecule may then be described by the range δwi = δp1δp2δp3 ... δpr. There are many such ranges corresponding to different states; a specific state may be denoted by the index i. Two molecules undergoing a collision can thus be denoted by (i, j) (Such an ordered pair is sometimes known as a constellation.) It is convenient to suppose that two molecules exert a negligible effect on each other unless their centre of gravities approach within a critical distance b. A collision therefore begins when the respective centres of gravity arrive at this critical distance, and is completed when they again reach this critical distance on their way apart. Under this model, a collision is completely described by the matrix , which refers to the constellation (i, j) before the collision, and the (in general different) constellation (k, l) after the collision. This notation is convenient in proving Boltzmann's H-theorem of statistical mechanics.
Attack by means of a deliberate collision
Types of attack by means of a deliberate collision include:
- with the body: unarmed striking, punching, kicking, martial arts, pugilism
- striking directly with a weapon, such as a sword, club or axe
- ramming with an object or vehicle, e.g.:
- a car deliberately crashing into a building to break into it
- a battering ram, medieval weapon used for breaking down large doors, also a modern version is used by police forces during raids
An attacking collision with a distant object can be achieved by throwing or launching a projectile.
See also
48 year-old Registered Nurse (Medical ) Rave from Pickering, enjoys to spend time individuals watching, new property for sale developers in singapore and cave diving. Finished a cruise liner experience that included passing by Chan Chan Archaeological Zone.
- Ballistic pendulum
- Coefficient of restitution
- Collision detection
- Collision (telecommunications)
- Car accident
- Elastic collision
- Friction
- Head-on collision
- Impact crater
40 year old Supply and Circulation Manager Courtney from Aberdeen, has several pursuits including bmx, property developers in new project launch singapore and actions. Finds travel a wonderful experience after visiting Central Sikhote-Alin.
- Impact event
- Inelastic collision
- Kinetic theory
- collisions between molecules - Mid-air collision
- Projectile
- Space debris
- Train wreck
Trying to invest in Singapore Actual Property , or are you attempting to promote, hire, invest, buy buy a Singapore property ? Properly then, you may have come to the fitting place in your seek for Singapore properties. Here, we are going to aid you find your dream Singapore property from our market itemizing of 1000's of Singapore properties in our Singapore real property database.
Overseas particular person who want to buy/ purchase a Restricted residential property in Sentosa Cove can acquire fast observe approval from Singapore Land Dealing Unit. Overseas particular person who want to purchase/ acquire a Restricted residential property in Sentosa Cove can apply for a long term social visit move underneath this Scheme to facilitate entry into Singapore. Foreign individual who want to apply for permanent residency in Singapore can contact SLA or MAS permitted institutions. The place you're shopping for property which is below development, the Singapore Academyof Regulation will maintain a portion of the acquisition monies as stakeholders till the expiryof the defects legal responsibility interval supplied in the Agreement/Contract. D19) Hougang / Punggol / Sengkang Condominium Common Room with Aircon
A international individual (any one who isn't a Singapore citizen, Singapore Company, Singapore restricted liability partnership or a Singapore society) will still want approval from the Singapore Land Authority (SLA) to purchase land-titled property such as houses, bungalows and vacant plots of land. Housing Improvement Board Properties SINGAPORE NON-PUBLIC RESIDENTIAL PROPERTIES Singapore firm; Singapore society. We provide invaluable services to expats who are considering relocation to Singapore For every kind of Singapore property related providers, we're there to obtain your name. You are positive to get one of the best Singapore properties with our help. RE/MAX Singapore Singapore Residential Business and Industrial Singapore citizen; Singapore Land Authority Thomson Highway, Singapore
Nevertheless, additionally it is a foul investment decision to go in too early. For instance you buy a property near one of the new MRT station location at the Thomson line. Because it takes 10 years to be accomplished, you might need difficulties renting that place out to pay off your mortgage payments. In addition, 10 years is a long time when something can occur including recession, new properties being introduced, modifications in interest rates etc. All these can have an adversarial impact on your property funding.
First, there are generally more rental transactions than gross sales transactions, to permit AV to be determined for every property based on comparable properties. Second, actions in sale costs are extra unstable than rentals. Therefore, using rental transactions to derive the AV helps to maintain property tax extra steady for property owners. If you are shopping for or trying to hire a property. It's tiring to call up individual property agent, prepare appointments, coordinate timing and to go for individual property viewing. What most individuals do is to have a property agent representing them who will organize and coordinate the viewings for all of the properties out there based mostly in your requirements & most well-liked timing. Rent Property District 12 Lease Property District thirteen
The brokers say that many Chinese language patrons are also investing abroad so they can personal property close to major instructional establishments. Some are buying houses close to top faculties — despite the fact that their youngsters are so little they can not walk but. Greater than 80 % of rich Chinese need to ship their children overseas to school, based on the Hurun Report, a Shanghai-based mostly publication. Chinese language patrons sometimes used to pick up properties within the $1 to $5 million vary in New York, typically shopping for two and three at a time for funding purposes, the brokers mentioned. Monika Tu, a dealer at high-end real estate agency Black Diamondz Property Concierge in Sydney, says that over the previous yr mainland Chinese language have develop into 80 % of her firm's business. WCEGA Plaza & Tower
An insurance coverage that covers the reinstatement worth or outstanding loan, whichever is decrease, within the event that the property search singapore (view site…) it insures is destroyed by fire. The coverage does not embody dwelling renovations, moveable household contents and personal belongings. Mortgage Insurance Credit bureau checks (e.g., Good payment data for bank cards / previous or existing loans, no previous blemishes corresponding to discharged bankrupts) A sign by the financial institution of the quantity of mortgage that you are eligible for. Nonetheless, an AIP doesn't constitute a binding loan offer. Additional checks and situations may be imposed by the financial institution, and the phrases of the formal supply will even rely upon the property that you simply intend to buy. Freehold / leasehold (999 years / 99 years)
Notes
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
References
- 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 Reissued (1979) New York: Dover ISBN 0-486-63896-0.
External links
- Three Dimensional Collision - Oblique inelastic collision between two homogeneous spheres.
- Two Dimensional Collision - Java applet that simulates elastic collisions.
- One Dimensional Collision - One Dimensional Collision Flash Applet.
- Two Dimensional Collision - Two Dimensional Collision Flash Applet.
ar:تصادم cs:Ráz těles da:Kollision de:Stoß (Physik) fa:برخورد fr:Collision ko:충돌 it:Urto lt:Smūgis hu:Ütközés nl:Botsing (natuurkunde) ja:衝突 pl:Zderzenie pt:Colisão ro:Coliziune ru:Удар simple:Collision sl:Trk sv:Stöt (mekanik) zh:碰撞



