Seismic moment: Difference between revisions
en>PixelBot m r2.7.3) (Robot: Removing ru:Сейсмический момент |
en>Addbot m Bot: Migrating 12 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q1481983 (Report Errors) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In [[cellular biology]] the term '''membrane transport''' refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of [[solutes]] such as [[ions]] and small [[molecules]] through [[biological membranes]], which are [[lipid bilayers]] that contain [[proteins]] embedded in them. The regulation of passage through the membrane is due to selective membrane permeability - a characteristic of biological membranes which allows them to separate substances of distinct chemical nature. In other words, they can be permeable to certain substances but not to others.<ref name="lodish">{{cite book| author = Lodish ''et al.'' | title = Biología celular y molecular | year = 2005 | edition = Buenos Aires: Médica Panamericana | isbn = 950-06-1374-3}}</ref><br /> | |||
The movements of most solutes through the membrane are mediated by [[membrane transport proteins]] which are specialized to varying degrees in the transport of specific molecules. As the diversity and [[physiology]] of the distinct [[Cell (biology)|cells]] is highly related to their capacities to attract different external elements, it is postulated that there is a group of specific transport proteins for each cell type and for every specific physiological stage<sup>[1]</sup>. This differential expression is [[regulated]] through the differential [[Transcription (genetics)|transcription]] of the [[genes]] coding for these proteins and its translation, for instance, through genetic-molecular mechanisms, but also at the cell biology level: the production of these proteins can be activated by [[cell signaling|cellular signaling pathways]], at the [[biochemical]] level, or even by being situated in [[cytoplasmic]] vesicles.<ref name="alberts">{{cite book | author = Alberts ''et al'' | title = Biología molecular de la célula | year = 2004 | edition = Barcelona: Omega | isbn = 8-428-21351-8}}</ref> | |||
== Background == | |||
Thermodynamically the flow of substances from one compartment to another can occur in the direction of a [[concentration]] or [[electrochemical]] [[gradient]] or against it. If the exchange of substances occurs in the direction of the gradient, that is, in the direction of decreasing potential, there is no requirement for an input of energy from outside the system; if, however, the transport is against the gradient, it will require the input of energy, metabolic energy in this case.<ref>{{cite book | author = Cromer, A.H. | title = Física para ciencias de la vida | year = 1996 | edition = Reverté ediciones | isbn = para España 84-291-1808-X }}</ref> | |||
For example, a classic chemical mechanism for separation that does not require the addition of external energy is dialysis. In this system a semipermeable membrane separates two solutions of different concentration of the same solute. If the membrane allows the passage of water but not the solute the water will move into the compartment with the greatest solute concentration in order to establish an [[Diffusion equilibrium|equilibrium]] in which the energy of the system is at a minimum. This takes place because the water moves from a high solvent concentration to a low one (in terms of the solute, the opposite occurs) and because the water is moving along a gradient there is no need for an external input of energy. | |||
[[File:Cell membrane scheme.png|thumb|250px|Diagram of a [[cell membrane]] <br /> | |||
1. phospholipid | |||
2. cholesterol | |||
3. glycolipid | |||
4. sugar | |||
5. polytopic protein (transmembrane protein) | |||
6. monotopic protein (here, a glycoprotein) | |||
7. monotopic protein anchored by a phospholipid | |||
8. peripheral monotopic protein (here, a glycoprotein.)]] | |||
The nature of biological membranes, especially that of its lipids, is [[amphiphilic]], as they form bilayers that contain an internal [[hydrophobic]] layer and an external [[hydrophilic]] layer. This structure makes transport possible by simple or [[passive diffusion]], which consists of the [[diffusion]] of substances through the membrane without expending metabolic energy and without the aid of transport proteins. If the transported substance has a net [[electrical charge]], it will move not only in response to a concentration gradient, but also to an [[electrochemical gradient]] due to the [[membrane potential]]. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Relative permeability of a phospholipid bilayer to various substances<ref name="lodish"/> | |||
|- | |||
!Type of substance | |||
!Examples | |||
!Behaviour | |||
|- | |||
|----- | |||
| Gases | |||
| CO<sub>2</sub>, N<sub>2</sub>, O<sub>2</sub> | |||
| Permeable | |||
|-bgcolor="#EFEFEF" | |||
| Small uncharged polar molecules | |||
| [[Urea]], [[water]], [[ethanol]] | |||
| Permeable, totally or partially | |||
|----- | |||
| Large uncharged polar molecules | |||
| [[glucose]], [[fructose]] | |||
| Not permeable | |||
|-bgcolor="#EFEFEF" | |||
| Ions | |||
| K<sup>+</sup>, Na<sup>+</sup>, Cl<sup>-</sup>, HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup> | |||
| Not permeable | |||
|----- | |||
| Charged polar molecules | |||
| [[Adenosine triphosphate|ATP]], [[amino acid]]s, [[glucose-6-phosphate]] | |||
| Not permeable | |||
|----- | |||
|}<br /> | |||
As few molecules are able to diffuse through a lipid membrane the majority of the transport processes involve transport proteins. These [[transmembrane proteins]] possess a large number of [[alpha helices]] immersed in the lipid matrix. In bacteria these proteins are present in the [[beta lamina]] form.<ref name="prescott">{{cite book| author = Prescott, L.M. | title = Microbiología | year = 1999 | edition = McGraw-Hill Interamericana de España, S.A.U. | isbn = 84-486-0261-7 }}</ref> This structure probably involves a conduit through hydrophilic protein environments that cause a disruption in the highly hydrophobic medium formed by the lipids.<sup>[1]</sup> These proteins can be involved in transport in a number of ways: they act as pumps driven by [[Adenosine triphosphate|ATP]], that is, by metabolic energy, or as channels of facilitated diffusion. | |||
== Thermodynamics == | |||
A physiological process can only take place if it complies with basic [[thermodynamic]] principles. Membrane transport obeys physical laws that define its capabilities and therefore its biological utility.<br /> | |||
A general principle of thermodynamics that governs the transfer of substances through membranes and other surfaces is that the exchange of [[Gibbs free energy|free energy]], Δ''G'', for the transport of a [[Mole (unit)|mole]] of a substance of concentration C<sub>1</sub> in a compartment to another compartment where it is present at C<sub>2</sub> is:<ref name="mathews"/> | |||
:<math>\Delta G = RT \log \frac{C_2}{C_1}</math> | |||
Where C<sub>2</sub> is less than C<sub>1</sub> Δ''G'' is negative, and the process is thermodynamically favorable. As the energy is transferred from one compartment to another, except where other factors intervene, an [[Diffusion equilibrium|equilibrium]] will be reached where C<sub>2</sub>=C<sub>1</sub>, and where ''G''=0. However, there are three circumstances under which this equilibrium will not be reached, circumstances which are vital for the ''in vivo'' functioning of biological membranes:<ref name="mathews"/> | |||
*The macromolecules on one side of the membrane can bond preferentially to a certain component of the membrane or chemically modify it. In this way, although the concentration of the solute may actually be different on both sides of the membrane, the availability of the solute is reduced in one of the compartments to such an extent that, for practical purposes, no gradient exists to drive transport. | |||
*A [[membrane potential|membrane electrical potential]] can exist which can influence ion distribution. For example, for the transport of ions from the exterior to the interior, it is possible that: | |||
:<math>\Delta G = RT \log \frac{C_{inside}}{C_{outside}}+ZF \Delta P</math> | |||
Where F is [[Faraday's constant]] and Δ''P'' the membrane potential in [[volts]]. If Δ''P'' is negative and Z is positive, the contribution of the term ''ZFΔP'' to Δ''G'' will be negative, that is, it will favor the transport of cations from the interior of the cell. So, if the potential difference is maintained, the equilibrium state Δ''G''=0 will not correspond to an equimolar concentration of ions on both sides of the membrane. | |||
*If a process with a negative Δ''G'' is coupled to the transport process then the global Δ''G'' will be modified. This situation is common in active transport and is described thus: | |||
:<math>\Delta G = RT \log \frac{C_{inside}}{C_{outside}}+\Delta G^b</math> | |||
Where Δ''G<sup>b</sup>'' corresponds to a favorable thermodynamic reaction, such as the hydrolysis of ATP, or the [[co-transport]] of a compound that is moved in the direction of its gradient. | |||
== Transport types == | |||
=== Passive diffusion === | |||
[[File:Diffusion.jpg|thumb|250px|A [[semipermeable membrane]] separates two compartments of different solute concentrations: over time, the solute will diffuse until equilibrium is reached.]] | |||
As mentioned above, passive diffusion is a spontaneous phenomenon that increases the [[entropy]] of a system and decreases the free energy.<ref name="mathews">{{cite book| author = Mathews C. K. | coauthors = Van Holde, K.E et Ahern, K.G | title = Bioquímica | edition = 3ª | year = 2003 | isbn = 84-7829-053-2}}</ref> The transport process is influenced by the characteristics of the transport substance and the nature of the bilayer. Membrane proteins (with the exception of channels - [[facilitated diffusion]]) are not involved in passive diffusion. The diffusion velocity of a pure phospholipid membrane will depend on: | |||
*concentration gradient, | |||
*hydrophobicity, | |||
*size, | |||
*charge, if the molecule has a net charge. | |||
===Active and co-transport=== | |||
In active transport a solute is moved against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, in doing so the transport proteins involved consume metabolic energy, usually ATP. In [[primary active transport]] the hydrolysis of the energy provider (e.g. ATP) takes place directly in order to transport the solute in question, for instance, when the transport proteins are [[ATPase]] [[enzymes]]. Where the hydrolysis of the energy provider is indirect as is the case in [[secondary active transport]], use is made of the energy stored in an electrochemical gradient. For example, in [[co-transport]] use is made of the gradients of certain solutes to transport a target compound against its gradient, causing the dissipation of the solute gradient. It may appear that, in this example, there is no energy use, but hydrolysis of the energy provider is required to establish the gradient of the solute transported along with the target compound. The gradient of the [[co-transport]]ed solute will be generated through the use of certain types of proteins called [[biochemical pumps]].<ref name="alberts"/> | |||
The discovery of the existence of this type of transporter protein came from the study of the kinetics of cross-membrane molecule transport. For certain solutes it was noted that the transport velocity reached a plateau at a particular concentration above which there was no significant increase in uptake rate, indicating a [[log curve]] type response. This was interpreted as showing that transport was mediated by the formation of a substrate-transporter complex, which is conceptually the same as the enzyme-substrate complex of [[enzyme kinetics]]. Therefore, each transport protein has an affinity constant for a solute that is equal to the concentration of the solute when the transport velocity is half its maximum value. This is equivalent in the case of an enzyme to the [[Michaelis-Menten constant]].<ref name="eckert">{{cite book | author = Randall D | coauthors = Burggren, W. et French, K. | title = Eckert Fisiología animal, | edition = 4ª | year = 1998 | editorial = | ubicación = | isbn = 84-486-0200-5}}</ref> | |||
Some important features of active transport in addition to its ability to intervene even against a gradient, its kinetics and the use of ATP, are its high selectivity and ease of selective pharmacological inhibition<ref name="eckert"/> | |||
==== Secondary active transporter proteins ==== | |||
[[File:TransportProteine.png|thumb| Uniport, symport, and antiport of molecules through membranes.]] | |||
Secondary active transporter proteins move two molecules at the same time: one against a gradient and the other with its gradient. They are distinguished according to the directionality of the two molecules: | |||
*[[antiporter]]: (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) move a molecule against its gradient and at the same time displaces one or more ions along its gradient. The molecules move in opposite directions. | |||
*[[symporter]]:move a molecule against its gradient while displacing one or more different ions along their gradient. The molecules move in the same direction. | |||
Both can be referred to as [[co-transporters]]. | |||
==== Pumps ==== | |||
[[File:Sodium Pump.svg|thumb|Simplified diagram of a [[sodium potassium pump]] showing alpha and beta units.]] | |||
A pump is a protein that hydrolyses ATP in order to transport a particular solute through a membrane in order to generate an electrochemical gradient to confer certain [[membrane potential]] characteristics on it. This gradient is of interest as an indicator of the state of the cell through parameters such as the [[Nernst potential]]. In terms of membrane transport the gradient is of interest as it contributes to increased system entropy in the [[co-transport]] of substances against their gradient. | |||
One of the most important pumps in animal cells is the [[sodium potassium pump]], that operates through the following mechanism:<ref name="lehninger">{{cite book | author = Lehninger, Albert | title= Principles of Biochemistry, 2nd Ed. | edition= Worth Publishers | year= 1993 | isbn= 0-87901-711-2}}</ref> | |||
#binding of three Na<sup>+</sup> ions to their active sites on the pump which are bound to ATP. | |||
#ATP is hydrolyzed leading to phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic side of the pump, this induces a structure change in the protein. The phosphorylation is caused by the transfer of the terminal group of ATP to a residue of [[aspartate]] in the transport protein and the subsequent release of ADP. | |||
#the structure change in the pump exposes the Na<sup>+</sup> to the exterior. The phosphorylated form of the pump has a low affinity for Na<sup>+</sup> ions so they are released. | |||
#once the Na<sup>+</sup> ions are liberated, the pump binds two molecules of K<sup>+</sup> to their respective bonding sites on the extracellular face of the transport protein.This causes the dephosphorylation of the pump, reverting it to its previous conformational state, transporting the K<sup>+</sup> ions into the cell. | |||
#The unphosphorylated form of the pump has a higher affinity for Na<sup>+</sup> ions than K<sup>+</sup> ions, so the two bound K<sup>+</sup> ions are released into the [[cytosol]]. ATP binds, and the process starts again. | |||
== Membrane selectivity == | |||
As the main characteristic of transport through a biological membrane is its selectivity and its subsequent behavior as a barrier for certain substances, the underlying physiology of the phenomenon has been studied extensively. Investigation into membrane selectivity have classically been divided into those relating to [[electrolytes]] and non-electrolytes. | |||
=== Electrolyte selectivity === | |||
The ionic channels define an internal diameter that permits the passage of small ions that is related to various characteristics of the ions that could potentially be transported. As the size of the ion is related to its chemical species, it could be assumed ''a priori'' that a channel whose pore diameter was sufficient to allow the passage of one ion would also allow the transfer of others of smaller size, however, this does not occur in the majority of cases. There are two characteristics alongside size that are important in the determination of the selectivity of the membrane pores: the facility for [[dehydration]] and the interaction of the ion with the internal charges of the pore.<ref name="eckert"/><br /> | |||
In order for an ion to pass through a pore it must dissociate itself from the water molecules that cover it in successive layers of [[solvation]]. The tendency to dehydrate, or the facility to do this, is related to the size of the ion: larger ions can do it more easily that the smaller ions, so that a pore with weak polar centres will preferentially allow passage of larger ions over the smaller ones.<ref name="eckert"/> | |||
When the interior of the channel is composed of polar groups from the side chains of the component amino acids,<ref name="lehninger"/> the interaction of a dehydrated ion with these centres can be more important than the facility for dehydration in conferring the specificity of the channel. For example, a channel made up of histidines and arginines, with positively charged groups, will selectively repel ions of the same polarity, but will facilitate the passage of negatively charged ions. Also, in this case, the smallest ions will be able to interact more closely due to the spatial arrangement of the molecule (stericity), which greatly increases the charge-charge interactions and therefore exaggerates the effect.<ref name="eckert"/> | |||
=== Non-electrolyte selectivity === | |||
Non-electrolytes, substances that generally are hydrophobic and lipophylic, usually pass through the membrane by dissolution in the lipid bilayer, and therefore, by passive diffusion. For those non-electrolytes whose transport through the membrane is mediated by a transport protein the ability to diffuse is, generally, dependent on the [[partition coefficient|partition coefficient K]]. | |||
Partially charged non-electrolytes, that are more or less polar, such as ethanol, methanol or urea, are able to pass through the membrane through aqueous channels immersed in the membrane. It is interesting to note that there is no effective regulation mechanism that limits this transport, which indicates an intrinsic vulnerability of the cells to the penetration of these molecules.<ref name="eckert"/> | |||
==Creation of Membrane Transport Proteins== | |||
There are several databases which attempt to construct phylogenetic trees detailing the creation of transporter proteins. One such resource is the [[Transporter Classification database]] <ref>{{cite web | |||
| url = http://www.TCDB.org | |||
| title = Transporter Classification Database | |||
| accessdate = 15 July 2010 | |||
| quote =}}</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Passive diffusion through the cell membrane]] | |||
*[[Cellular transport]] | |||
*[[Trans-membrane transport]] | |||
== References == | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
{{Membrane transport}} | |||
[[Category:Membrane biology|Membrane transport]] | |||
{{Link GA|es}} | |||
Revision as of 23:11, 26 February 2013
In cellular biology the term membrane transport refers to the collection of mechanisms that regulate the passage of solutes such as ions and small molecules through biological membranes, which are lipid bilayers that contain proteins embedded in them. The regulation of passage through the membrane is due to selective membrane permeability - a characteristic of biological membranes which allows them to separate substances of distinct chemical nature. In other words, they can be permeable to certain substances but not to others.[1]
The movements of most solutes through the membrane are mediated by membrane transport proteins which are specialized to varying degrees in the transport of specific molecules. As the diversity and physiology of the distinct cells is highly related to their capacities to attract different external elements, it is postulated that there is a group of specific transport proteins for each cell type and for every specific physiological stage[1]. This differential expression is regulated through the differential transcription of the genes coding for these proteins and its translation, for instance, through genetic-molecular mechanisms, but also at the cell biology level: the production of these proteins can be activated by cellular signaling pathways, at the biochemical level, or even by being situated in cytoplasmic vesicles.[2]
Background
Thermodynamically the flow of substances from one compartment to another can occur in the direction of a concentration or electrochemical gradient or against it. If the exchange of substances occurs in the direction of the gradient, that is, in the direction of decreasing potential, there is no requirement for an input of energy from outside the system; if, however, the transport is against the gradient, it will require the input of energy, metabolic energy in this case.[3] For example, a classic chemical mechanism for separation that does not require the addition of external energy is dialysis. In this system a semipermeable membrane separates two solutions of different concentration of the same solute. If the membrane allows the passage of water but not the solute the water will move into the compartment with the greatest solute concentration in order to establish an equilibrium in which the energy of the system is at a minimum. This takes place because the water moves from a high solvent concentration to a low one (in terms of the solute, the opposite occurs) and because the water is moving along a gradient there is no need for an external input of energy.

1. phospholipid 2. cholesterol 3. glycolipid 4. sugar 5. polytopic protein (transmembrane protein) 6. monotopic protein (here, a glycoprotein) 7. monotopic protein anchored by a phospholipid 8. peripheral monotopic protein (here, a glycoprotein.)
The nature of biological membranes, especially that of its lipids, is amphiphilic, as they form bilayers that contain an internal hydrophobic layer and an external hydrophilic layer. This structure makes transport possible by simple or passive diffusion, which consists of the diffusion of substances through the membrane without expending metabolic energy and without the aid of transport proteins. If the transported substance has a net electrical charge, it will move not only in response to a concentration gradient, but also to an electrochemical gradient due to the membrane potential.
| Type of substance | Examples | Behaviour |
|---|---|---|
| Gases | CO2, N2, O2 | Permeable |
| Small uncharged polar molecules | Urea, water, ethanol | Permeable, totally or partially |
| Large uncharged polar molecules | glucose, fructose | Not permeable |
| Ions | K+, Na+, Cl-, HCO3- | Not permeable |
| Charged polar molecules | ATP, amino acids, glucose-6-phosphate | Not permeable |
As few molecules are able to diffuse through a lipid membrane the majority of the transport processes involve transport proteins. These transmembrane proteins possess a large number of alpha helices immersed in the lipid matrix. In bacteria these proteins are present in the beta lamina form.[4] This structure probably involves a conduit through hydrophilic protein environments that cause a disruption in the highly hydrophobic medium formed by the lipids.[1] These proteins can be involved in transport in a number of ways: they act as pumps driven by ATP, that is, by metabolic energy, or as channels of facilitated diffusion.
Thermodynamics
A physiological process can only take place if it complies with basic thermodynamic principles. Membrane transport obeys physical laws that define its capabilities and therefore its biological utility.
A general principle of thermodynamics that governs the transfer of substances through membranes and other surfaces is that the exchange of free energy, ΔG, for the transport of a mole of a substance of concentration C1 in a compartment to another compartment where it is present at C2 is:[5]
Where C2 is less than C1 ΔG is negative, and the process is thermodynamically favorable. As the energy is transferred from one compartment to another, except where other factors intervene, an equilibrium will be reached where C2=C1, and where G=0. However, there are three circumstances under which this equilibrium will not be reached, circumstances which are vital for the in vivo functioning of biological membranes:[5]
- The macromolecules on one side of the membrane can bond preferentially to a certain component of the membrane or chemically modify it. In this way, although the concentration of the solute may actually be different on both sides of the membrane, the availability of the solute is reduced in one of the compartments to such an extent that, for practical purposes, no gradient exists to drive transport.
- A membrane electrical potential can exist which can influence ion distribution. For example, for the transport of ions from the exterior to the interior, it is possible that:
Where F is Faraday's constant and ΔP the membrane potential in volts. If ΔP is negative and Z is positive, the contribution of the term ZFΔP to ΔG will be negative, that is, it will favor the transport of cations from the interior of the cell. So, if the potential difference is maintained, the equilibrium state ΔG=0 will not correspond to an equimolar concentration of ions on both sides of the membrane.
- If a process with a negative ΔG is coupled to the transport process then the global ΔG will be modified. This situation is common in active transport and is described thus:
Where ΔGb corresponds to a favorable thermodynamic reaction, such as the hydrolysis of ATP, or the co-transport of a compound that is moved in the direction of its gradient.
Transport types
Passive diffusion
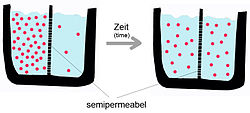
As mentioned above, passive diffusion is a spontaneous phenomenon that increases the entropy of a system and decreases the free energy.[5] The transport process is influenced by the characteristics of the transport substance and the nature of the bilayer. Membrane proteins (with the exception of channels - facilitated diffusion) are not involved in passive diffusion. The diffusion velocity of a pure phospholipid membrane will depend on:
- concentration gradient,
- hydrophobicity,
- size,
- charge, if the molecule has a net charge.
Active and co-transport
In active transport a solute is moved against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, in doing so the transport proteins involved consume metabolic energy, usually ATP. In primary active transport the hydrolysis of the energy provider (e.g. ATP) takes place directly in order to transport the solute in question, for instance, when the transport proteins are ATPase enzymes. Where the hydrolysis of the energy provider is indirect as is the case in secondary active transport, use is made of the energy stored in an electrochemical gradient. For example, in co-transport use is made of the gradients of certain solutes to transport a target compound against its gradient, causing the dissipation of the solute gradient. It may appear that, in this example, there is no energy use, but hydrolysis of the energy provider is required to establish the gradient of the solute transported along with the target compound. The gradient of the co-transported solute will be generated through the use of certain types of proteins called biochemical pumps.[2]
The discovery of the existence of this type of transporter protein came from the study of the kinetics of cross-membrane molecule transport. For certain solutes it was noted that the transport velocity reached a plateau at a particular concentration above which there was no significant increase in uptake rate, indicating a log curve type response. This was interpreted as showing that transport was mediated by the formation of a substrate-transporter complex, which is conceptually the same as the enzyme-substrate complex of enzyme kinetics. Therefore, each transport protein has an affinity constant for a solute that is equal to the concentration of the solute when the transport velocity is half its maximum value. This is equivalent in the case of an enzyme to the Michaelis-Menten constant.[6]
Some important features of active transport in addition to its ability to intervene even against a gradient, its kinetics and the use of ATP, are its high selectivity and ease of selective pharmacological inhibition[6]
Secondary active transporter proteins
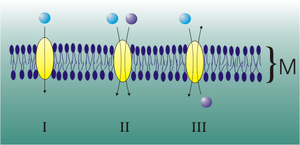
Secondary active transporter proteins move two molecules at the same time: one against a gradient and the other with its gradient. They are distinguished according to the directionality of the two molecules:
- antiporter: (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) move a molecule against its gradient and at the same time displaces one or more ions along its gradient. The molecules move in opposite directions.
- symporter:move a molecule against its gradient while displacing one or more different ions along their gradient. The molecules move in the same direction.
Both can be referred to as co-transporters.
Pumps

A pump is a protein that hydrolyses ATP in order to transport a particular solute through a membrane in order to generate an electrochemical gradient to confer certain membrane potential characteristics on it. This gradient is of interest as an indicator of the state of the cell through parameters such as the Nernst potential. In terms of membrane transport the gradient is of interest as it contributes to increased system entropy in the co-transport of substances against their gradient. One of the most important pumps in animal cells is the sodium potassium pump, that operates through the following mechanism:[7]
- binding of three Na+ ions to their active sites on the pump which are bound to ATP.
- ATP is hydrolyzed leading to phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic side of the pump, this induces a structure change in the protein. The phosphorylation is caused by the transfer of the terminal group of ATP to a residue of aspartate in the transport protein and the subsequent release of ADP.
- the structure change in the pump exposes the Na+ to the exterior. The phosphorylated form of the pump has a low affinity for Na+ ions so they are released.
- once the Na+ ions are liberated, the pump binds two molecules of K+ to their respective bonding sites on the extracellular face of the transport protein.This causes the dephosphorylation of the pump, reverting it to its previous conformational state, transporting the K+ ions into the cell.
- The unphosphorylated form of the pump has a higher affinity for Na+ ions than K+ ions, so the two bound K+ ions are released into the cytosol. ATP binds, and the process starts again.
Membrane selectivity
As the main characteristic of transport through a biological membrane is its selectivity and its subsequent behavior as a barrier for certain substances, the underlying physiology of the phenomenon has been studied extensively. Investigation into membrane selectivity have classically been divided into those relating to electrolytes and non-electrolytes.
Electrolyte selectivity
The ionic channels define an internal diameter that permits the passage of small ions that is related to various characteristics of the ions that could potentially be transported. As the size of the ion is related to its chemical species, it could be assumed a priori that a channel whose pore diameter was sufficient to allow the passage of one ion would also allow the transfer of others of smaller size, however, this does not occur in the majority of cases. There are two characteristics alongside size that are important in the determination of the selectivity of the membrane pores: the facility for dehydration and the interaction of the ion with the internal charges of the pore.[6]
In order for an ion to pass through a pore it must dissociate itself from the water molecules that cover it in successive layers of solvation. The tendency to dehydrate, or the facility to do this, is related to the size of the ion: larger ions can do it more easily that the smaller ions, so that a pore with weak polar centres will preferentially allow passage of larger ions over the smaller ones.[6]
When the interior of the channel is composed of polar groups from the side chains of the component amino acids,[7] the interaction of a dehydrated ion with these centres can be more important than the facility for dehydration in conferring the specificity of the channel. For example, a channel made up of histidines and arginines, with positively charged groups, will selectively repel ions of the same polarity, but will facilitate the passage of negatively charged ions. Also, in this case, the smallest ions will be able to interact more closely due to the spatial arrangement of the molecule (stericity), which greatly increases the charge-charge interactions and therefore exaggerates the effect.[6]
Non-electrolyte selectivity
Non-electrolytes, substances that generally are hydrophobic and lipophylic, usually pass through the membrane by dissolution in the lipid bilayer, and therefore, by passive diffusion. For those non-electrolytes whose transport through the membrane is mediated by a transport protein the ability to diffuse is, generally, dependent on the partition coefficient K. Partially charged non-electrolytes, that are more or less polar, such as ethanol, methanol or urea, are able to pass through the membrane through aqueous channels immersed in the membrane. It is interesting to note that there is no effective regulation mechanism that limits this transport, which indicates an intrinsic vulnerability of the cells to the penetration of these molecules.[6]
Creation of Membrane Transport Proteins
There are several databases which attempt to construct phylogenetic trees detailing the creation of transporter proteins. One such resource is the Transporter Classification database [8]
See also
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 2.0 2.1 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 7.0 7.1 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ Template:Cite web


