Eddington number: Difference between revisions
'named' is more appropriate than 'christened' |
en>Bibcode Bot m Adding 0 arxiv eprint(s), 1 bibcode(s) and 0 doi(s). Did it miss something? Report bugs, errors, and suggestions at User talk:Bibcode Bot |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:3D Vector.svg|right|thumb|300px|Every vector '''a''' in three dimensions is a [[linear combination]] of the standard basis vectors '''i''', '''j''', and '''k'''.]] | |||
In [[mathematics]], the '''standard basis''' (also called '''natural basis''' or '''canonical basis''') for a [[Euclidean space]] is the set of [[unit vector]]s pointing in the direction of the axes of a [[Cartesian coordinate system]]. For example, the standard basis for the [[Euclidean plane]] is formed by vectors | |||
:<math>\mathbf{e}_x = (1,0),\quad \mathbf{e}_y = (0,1),</math> | |||
and the standard basis for [[three-dimensional space]] is formed by vectors | |||
:<math>\mathbf{e}_x = (1,0,0),\quad \mathbf{e}_y = (0,1,0),\quad \mathbf{e}_z=(0,0,1).</math> | |||
Here the vector '''e'''<sub>''x''</sub> points in the ''x'' direction, the vector '''e'''<sub>''y''</sub> points in the ''y'' direction, and the vector '''e'''<sub>''z''</sub> points in the ''z'' direction. There are several common [[mathematical notation|notations]] for these vectors, including {'''e'''<sub>''x''</sub>, '''e'''<sub>''y''</sub>, '''e'''<sub>''z''</sub>}, {'''e'''<sub>1</sub>, '''e'''<sub>2</sub>, '''e'''<sub>3</sub>}, {'''i''', '''j''', '''k'''}, and {'''x''', '''y''', '''z'''}. These vectors are sometimes written with a [[circumflex|hat]] to emphasize their status as unit vectors. Each of these vectors is sometimes referred to as the [[Versor#Definition in geometry and physics|versor]] of the corresponding Cartesian axis. | |||
These vectors are a [[basis (linear algebra)|basis]] in the sense that any other vector can be expressed uniquely as a [[linear combination]] of these. For example, every vector '''v''' in three-dimensional space can be written uniquely as | |||
:<math>v_x\,\mathbf{e}_x + v_y\,\mathbf{e}_y + v_z\,\mathbf{e}_z,</math> | |||
the [[scalar (mathematics)|scalars]] ''v''<sub>''x''</sub>, ''v''<sub>''y''</sub>, ''v''<sub>''z''</sub> being the [[scalar component]]s of the vector '''v'''. | |||
In <math>n</math>-[[dimension (linear algebra)|dimensional]] Euclidean space, the standard basis consists of ''n'' distinct vectors | |||
:<math>\{ \mathbf{e}_i : 1\leq i\leq n\},</math> | |||
where '''e'''<sub>''i''</sub> denotes the vector with a 1 in the <math>i</math>th [[coordinate]] and 0's elsewhere. | |||
== Properties == | |||
By definition, the standard basis is a [[sequence]] of [[orthogonal]] [[unit vectors]]. In other words, it is an [[ordered basis|ordered]] and [[orthonormal basis|orthonormal]] basis. | |||
However, an ordered orthonormal basis is not necessarily a standard basis. For instance the two vectors, | |||
:<math>v_1 = \left( {\sqrt 3 \over 2} , {1 \over 2} \right) \,</math> | |||
:<math>v_2 = \left( {1 \over 2} , {-\sqrt 3 \over 2} \right) \,</math> | |||
are orthogonal unit vectors, but the orthonormal basis they form does not meet the definition of standard basis. | |||
==Generalizations== | |||
There is a ''standard'' basis also for the ring of [[polynomial]]s in ''n'' indeterminates over a [[field (mathematics)|field]], namely the [[monomial]]s. | |||
All of the preceding are special cases of the family | |||
:<math>{(e_i)}_{i\in I}= ( (\delta_{ij} )_{j \in I} )_{i \in I}</math> | |||
where <math>I</math> is any set and <math>\delta_{ij}</math> is the [[Kronecker delta]], equal to zero whenever ''i≠j'' and equal to 1 if ''i=j''. | |||
This family is the ''canonical'' basis of the ''R''-module ([[free module]]) | |||
:<math>R^{(I)}</math> | |||
of all families | |||
:<math>f=(f_i)</math> | |||
from ''I'' into a [[ring (mathematics)|ring]] ''R'', which are zero except for a finite number of indices, if we interpret 1 as 1<sub>''R''</sub>, the unit in ''R''. | |||
==Other usages== | |||
The existence of other 'standard' bases has become a topic of interest in [[algebraic geometry]], beginning with work of [[W. V. D. Hodge|Hodge]] from 1943 on [[Grassmannian]]s. It is now a part of [[representation theory]] called ''standard monomial theory''. The idea of standard basis in the [[universal enveloping algebra]] of a [[Lie algebra]] is established by the [[Poincaré–Birkhoff–Witt theorem]]. | |||
[[Gröbner basis|Gröbner bases]] are also sometimes called standard bases. | |||
In [[physics]], the standard basis vectors for a given Euclidean space are sometimes referred to as the [[Versor (physics)|versors]] of the axes of the corresponding Cartesian coordinate system. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Canonical units]] | |||
*[[Examples of vector spaces#Generalized coordinate space]] | |||
==References== | |||
*{{cite book | |||
| last = Ryan | |||
| first = Patrick J. | |||
| title = Euclidean and non-Euclidean geometry: an analytical approach | |||
| publisher = Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press | |||
| date = 1986 | |||
| pages = | |||
| isbn = 0-521-27635-7 | |||
}} (page 198) | |||
*{{cite book | |||
| last = Schneider | |||
| first = Philip J. | |||
| coauthors = Eberly, David H. | |||
| title = Geometric tools for computer graphics | |||
| publisher = Amsterdam; Boston: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers | |||
| date = 2003 | |||
| pages = | |||
| isbn = 1-55860-594-0 | |||
}} (page 112) | |||
[[Category:Linear algebra]] | |||
Revision as of 17:14, 26 July 2013
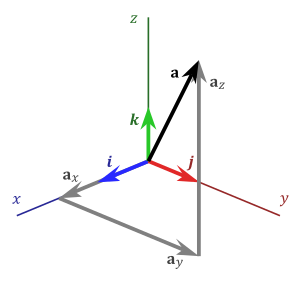
In mathematics, the standard basis (also called natural basis or canonical basis) for a Euclidean space is the set of unit vectors pointing in the direction of the axes of a Cartesian coordinate system. For example, the standard basis for the Euclidean plane is formed by vectors
and the standard basis for three-dimensional space is formed by vectors
Here the vector ex points in the x direction, the vector ey points in the y direction, and the vector ez points in the z direction. There are several common notations for these vectors, including {ex, ey, ez}, {e1, e2, e3}, {i, j, k}, and {x, y, z}. These vectors are sometimes written with a hat to emphasize their status as unit vectors. Each of these vectors is sometimes referred to as the versor of the corresponding Cartesian axis.
These vectors are a basis in the sense that any other vector can be expressed uniquely as a linear combination of these. For example, every vector v in three-dimensional space can be written uniquely as
the scalars vx, vy, vz being the scalar components of the vector v.
In -dimensional Euclidean space, the standard basis consists of n distinct vectors
where ei denotes the vector with a 1 in the th coordinate and 0's elsewhere.
Properties
By definition, the standard basis is a sequence of orthogonal unit vectors. In other words, it is an ordered and orthonormal basis.
However, an ordered orthonormal basis is not necessarily a standard basis. For instance the two vectors,
are orthogonal unit vectors, but the orthonormal basis they form does not meet the definition of standard basis.
Generalizations
There is a standard basis also for the ring of polynomials in n indeterminates over a field, namely the monomials.
All of the preceding are special cases of the family
where is any set and is the Kronecker delta, equal to zero whenever i≠j and equal to 1 if i=j. This family is the canonical basis of the R-module (free module)
of all families
from I into a ring R, which are zero except for a finite number of indices, if we interpret 1 as 1R, the unit in R.
Other usages
The existence of other 'standard' bases has become a topic of interest in algebraic geometry, beginning with work of Hodge from 1943 on Grassmannians. It is now a part of representation theory called standard monomial theory. The idea of standard basis in the universal enveloping algebra of a Lie algebra is established by the Poincaré–Birkhoff–Witt theorem.
Gröbner bases are also sometimes called standard bases.
In physics, the standard basis vectors for a given Euclidean space are sometimes referred to as the versors of the axes of the corresponding Cartesian coordinate system.
See also
References
- 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 (page 198)
- 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 (page 112)












