Integer: Difference between revisions
en>Shafaet |
en>I dream of horses m Reverted edits by 121.96.187.166 (talk): unexplained content removal (HG) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Other uses}} | |||
In the [[mathematics|mathematical]] field of [[numerical analysis]], '''interpolation''' is a method of constructing new data points within the range of a [[discrete set]] of known data points. | |||
In [[engineering]] and [[science]], one often has a number of data points, obtained by [[sampling (statistics)|sampling]] or [[experimentation]], which represent the values of a function for a limited number of values of the independent variable. It is often required to '''interpolate''' (i.e. estimate) the value of that function for an intermediate value of the independent variable. This may be achieved by [[curve fitting]] or [[regression analysis]]. | |||
A different problem which is closely related to interpolation is the approximation of a complicated function by a simple function. Suppose the formula for some given function is known, but too complex to evaluate efficiently. A few known data points from the original function can be used to create an interpolation based on a simpler function. Of course, when a simple function is used to estimate data points from the original, interpolation errors are usually present; however, depending on the problem domain and the interpolation method used, the gain in simplicity may be of greater value than the resultant loss in accuracy. | |||
There is also another very different kind of interpolation in mathematics, namely the "interpolation of operators". The classical results about interpolation of operators are the [[Riesz–Thorin theorem]] and the [[Marcinkiewicz theorem]]. There are also many other subsequent results. | |||
[[Image:Splined epitrochoid.svg|300px|thumb|An interpolation of a finite set of points on an [[epitrochoid]]. Points through which curve is [[spline (mathematics)|splined]] are red; the blue curve connecting them is interpolation.]] | |||
==Example== | |||
For example, suppose we have a table like this, which gives some values of an unknown function ''f''. | |||
[[Image:Interpolation Data.svg|right|thumb|230px|Plot of the data points as given in the table.]] | |||
{| cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0 | |||
|width="20px"| | |||
! ''x'' | |||
|width="10px"| | |||
!colspan=3 align=center| ''f''(''x'') | |||
|- | |||
| || 0 || ||align=right| 0 | |||
|- | |||
| || 1 || ||align=right| 0 || . || 8415 | |||
|- | |||
| || 2 || ||align=right| 0 || . || 9093 | |||
|- | |||
| || 3 || ||align=right| 0 || . ||1411 | |||
|- | |||
| || 4 || ||align=right| −0 || . || 7568 | |||
|- | |||
| || 5 || ||align=right| −0 || . || 9589 | |||
|- | |||
| || 6 || ||align=right| −0 || . || 2794 | |||
|} | |||
Interpolation provides a means of estimating the function at intermediate points, such as ''x'' = 2.5. | |||
There are many different interpolation methods, some of which are described below. Some of the concerns to take into account when choosing an appropriate [[algorithm]] are: How accurate is the method? How expensive is it? How [[smooth function|smooth]] is the interpolant? How many data points are needed? | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
===Piecewise constant interpolation=== | |||
[[Image:Piecewise constant.svg|thumb|right|Piecewise constant interpolation, or [[nearest-neighbor interpolation]].]] | |||
{{details|Nearest-neighbor interpolation}} | |||
The simplest interpolation method is to locate the nearest data value, and assign the same value. In simple problems, this method is unlikely to be used, as linear interpolation (see below) is almost as easy, but in higher dimensional [[multivariate interpolation]], this could be a favourable choice for its speed and simplicity. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
===Linear interpolation=== | |||
[[Image:Interpolation example linear.svg|right|thumb|230px|Plot of the data with linear interpolation superimposed]] | |||
{{Main|Linear interpolation}} | |||
One of the simplest methods is [[linear]] interpolation (sometimes known as lerp). Consider the above example of estimating ''f''(2.5). Since 2.5 is midway between 2 and 3, it is reasonable to take ''f''(2.5) midway between ''f''(2) = 0.9093 and ''f''(3) = 0.1411, which yields 0.5252. | |||
Generally, linear interpolation takes two data points, say (''x''<sub>''a''</sub>,''y''<sub>''a''</sub>) and (''x''<sub>''b''</sub>,''y''<sub>''b''</sub>), and the interpolant is given by: | |||
:<math> y = y_a + \left( y_b-y_a \right) \frac{x-x_a}{x_b-x_a} \text{ at the point } \left( x,y \right) </math> | |||
Linear interpolation is quick and easy, but it is not very precise. Another disadvantage is that the interpolant is not [[derivative|differentiable]] at the point ''x''<sub>''k''</sub>. | |||
The following error estimate shows that linear interpolation is not very precise. Denote the function which we want to interpolate by ''g'', and suppose that ''x'' lies between ''x''<sub>''a''</sub> and ''x''<sub>''b''</sub> and that ''g'' is twice continuously differentiable. Then the linear interpolation error is | |||
:<math> |f(x)-g(x)| \le C(x_b-x_a)^2 \quad\text{where}\quad C = \frac18 \max_{y\in[x_a,x_b]} |g''(y)|. </math> | |||
In words, the error is proportional to the square of the distance between the data points. The error in some other methods, including polynomial interpolation and spline interpolation (described below), is proportional to higher powers of the distance between the data points. These methods also produce smoother interpolants. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
===Polynomial interpolation=== | |||
[[Image:Interpolation example polynomial.svg|right|thumb|230px|Plot of the data with polynomial interpolation applied]] | |||
{{Main|Polynomial interpolation}} | |||
Polynomial interpolation is a generalization of linear interpolation. Note that the linear interpolant is a [[linear function]]. We now replace this interpolant with a [[polynomial]] of higher [[degree of a polynomial|degree]]. | |||
Consider again the problem given above. The following sixth degree polynomial goes through all the seven points: | |||
:<math> f(x) = -0.0001521 x^6 - 0.003130 x^5 + 0.07321 x^4 - 0.3577 x^3 + 0.2255 x^2 + 0.9038 x. </math> | |||
<!-- Coefficients are 0, 0.903803333333334, 0.22549749999997, -0.35772291666664, 0.07321458333332, -0.00313041666667, -0.00015208333333. --> | |||
Substituting ''x'' = 2.5, we find that ''f''(2.5) = 0.5965. | |||
Generally, if we have ''n'' data points, there is exactly one polynomial of degree at most ''n''−1 going through all the data points. The interpolation error is proportional to the distance between the data points to the power ''n''. Furthermore, the interpolant is a polynomial and thus infinitely differentiable. So, we see that polynomial interpolation overcomes most of the problems of linear interpolation. | |||
However, polynomial interpolation also has some disadvantages. Calculating the interpolating polynomial is computationally expensive (see [[computational complexity]]) compared to linear interpolation. Furthermore, polynomial interpolation may exhibit oscillatory artifacts, especially at the end points (see [[Runge's phenomenon]]). More generally, the shape of the resulting curve, especially for very high or low values of the independent variable, may be contrary to commonsense, i.e. to what is known about the experimental system which has generated the data points. These disadvantages can be reduced by using spline interpolation or restricting attention to [[Chebyshev polynomials]]. | |||
<br clear="all" /> | |||
===Spline interpolation=== | |||
[[Image:Interpolation example spline.svg|right|thumb|230px|Plot of the data with spline interpolation applied]] | |||
{{Main|Spline interpolation}} | |||
Remember that linear interpolation uses a linear function for each of intervals [''x''<sub>''k''</sub>,''x''<sub>''k+1''</sub>]. Spline interpolation uses low-degree polynomials in each of the intervals, and chooses the polynomial pieces such that they fit smoothly together. The resulting function is called a [[spline (mathematics)|spline]]. | |||
For instance, the [[natural cubic spline]] is [[piecewise]] cubic and twice continuously differentiable. Furthermore, its second derivative is zero at the end points. The natural cubic spline interpolating the points in the table above is given by | |||
: <math> f(x) = \begin{cases} | |||
-0.1522 x^3 + 0.9937 x, & \text{if } x \in [0,1], \\ | |||
-0.01258 x^3 - 0.4189 x^2 + 1.4126 x - 0.1396, & \text{if } x \in [1,2], \\ | |||
0.1403 x^3 - 1.3359 x^2 + 3.2467 x - 1.3623, & \text{if } x \in [2,3], \\ | |||
0.1579 x^3 - 1.4945 x^2 + 3.7225 x - 1.8381, & \text{if } x \in [3,4], \\ | |||
0.05375 x^3 -0.2450 x^2 - 1.2756 x + 4.8259, & \text{if } x \in [4,5], \\ | |||
-0.1871 x^3 + 3.3673 x^2 - 19.3370 x + 34.9282, & \text{if } x \in [5,6]. | |||
\end{cases} </math> | |||
In this case we get ''f''(2.5) = 0.5972. | |||
Like polynomial interpolation, spline interpolation incurs a smaller error than linear interpolation and the interpolant is smoother. However, the interpolant is easier to evaluate than the high-degree polynomials used in polynomial interpolation. It also does not suffer from [[Runge's phenomenon]]. | |||
{{Clear}} | |||
==Interpolation via Gaussian processes== | |||
[[Gaussian process]] is a powerful non-linear interpolation tool. Many popular interpolation tools are actually equivalent to particular Gaussian processes. Gaussian processes can be used not only for fitting an interpolant that passes exactly through the given data points but also for regression, i.e., for fitting a curve through noisy data. In the geostatistics community Gaussian process regression is also known as [[Kriging]]. | |||
==Other forms of interpolation== | |||
Other forms of interpolation can be constructed by picking a different class of interpolants. For instance, rational interpolation is '''interpolation''' by [[rational function]]s, and [[trigonometric interpolation]] is interpolation by [[trigonometric polynomial]]s. Another possibility is to use [[wavelet]]s. | |||
The [[Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula]] can be used if the number of data points is infinite. | |||
[[Multivariate interpolation]] is the interpolation of functions of more than one variable. Methods include [[bilinear interpolation]] and [[bicubic interpolation]] in two dimensions, and [[trilinear interpolation]] in three dimensions. | |||
Sometimes, we know not only the value of the function that we want to interpolate, at some points, but also its derivative. This leads to [[Hermite interpolation]] problems. | |||
When each data point is itself a function, it can be useful to see the interpolation problem as a partial [[advection]] problem between each data point. This idea leads to the [[displacement interpolation]] problem used in [[Transportation theory (mathematics)|transportation theory]]. | |||
==Interpolation in digital signal processing== | |||
In the domain of digital signal processing, the term interpolation refers to the process of converting a sampled digital signal (such as a sampled audio signal) to a higher sampling rate ([[Upsampling]]) using various digital filtering techniques (e.g., convolution with a frequency-limited impulse signal). In this application there is a specific requirement that the harmonic content of the original signal be preserved without creating aliased harmonic content of the original signal above the original Nyquist limit of the signal (i.e., above fs/2 of the original signal sample rate). An early and fairly elementary discussion on this subject can be found in Rabiner and Crochiere's book ''Multirate Digital Signal Processing''.<ref>[http://www.amazon.com/Multirate-Digital-Signal-Processing-Crochiere/dp/0136051626 R.E. Crochiere and L.R. Rabiner. (1983). Multirate Digital Signal Processing. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice–Hall.]</ref> | |||
==Related concepts== | |||
The term ''[[extrapolation]]'' is used if we want to find data points outside the range of known data points. | |||
In [[curve fitting]] problems, the constraint that the interpolant has to go exactly through the data points is relaxed. It is only required to approach the data points as closely as possible (within some other constraints). This requires parameterizing the potential interpolants and having some way of measuring the error. In the simplest case this leads to [[least squares]] approximation. | |||
[[Approximation theory]] studies how to find the best approximation to a given function by another function from some predetermined class, and how good this approximation is. This clearly yields a bound on how well the interpolant can approximate the unknown function. | |||
==See also== | |||
{{Div col|cols=2}} | |||
* [[Barycentric_coordinate_system_%28mathematics%29|Barycentric coordinates – for interpolating within on a triangle or tetrahedron]] | |||
* [[Bilinear interpolation]] | |||
* [[Brahmagupta's interpolation formula]] | |||
* [[Extrapolation]] | |||
* [[Imputation (statistics)]] | |||
* [[Missing data]] | |||
* [[Multivariate interpolation]] | |||
* [[Newton–Cotes formulas]] | |||
* [[Polynomial interpolation]] | |||
* [[Simple rational approximation]] | |||
{{Div col end}} | |||
==References== | |||
<references /> | |||
==External links== | |||
* [http://sol.gfxile.net/interpolation/index.html Sol Tutorials - Interpolation Tricks] | |||
[[Category:Interpolation| ]] | |||
[[Category:Video]] | |||
[[Category:Video signal]] | |||
Revision as of 03:10, 17 January 2014
I'm Fernando (21) from Seltjarnarnes, Iceland.
I'm learning Norwegian literature at a local college and I'm just about to graduate.
I have a part time job in a the office.
my site; wellness [continue reading this..]
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a method of constructing new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one often has a number of data points, obtained by sampling or experimentation, which represent the values of a function for a limited number of values of the independent variable. It is often required to interpolate (i.e. estimate) the value of that function for an intermediate value of the independent variable. This may be achieved by curve fitting or regression analysis.
A different problem which is closely related to interpolation is the approximation of a complicated function by a simple function. Suppose the formula for some given function is known, but too complex to evaluate efficiently. A few known data points from the original function can be used to create an interpolation based on a simpler function. Of course, when a simple function is used to estimate data points from the original, interpolation errors are usually present; however, depending on the problem domain and the interpolation method used, the gain in simplicity may be of greater value than the resultant loss in accuracy.
There is also another very different kind of interpolation in mathematics, namely the "interpolation of operators". The classical results about interpolation of operators are the Riesz–Thorin theorem and the Marcinkiewicz theorem. There are also many other subsequent results.

Example
For example, suppose we have a table like this, which gives some values of an unknown function f.
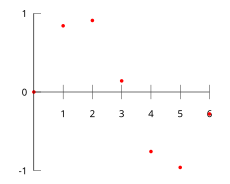
| x | f(x) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | ||||
| 1 | 0 | . | 8415 | ||
| 2 | 0 | . | 9093 | ||
| 3 | 0 | . | 1411 | ||
| 4 | −0 | . | 7568 | ||
| 5 | −0 | . | 9589 | ||
| 6 | −0 | . | 2794 | ||
Interpolation provides a means of estimating the function at intermediate points, such as x = 2.5.
There are many different interpolation methods, some of which are described below. Some of the concerns to take into account when choosing an appropriate algorithm are: How accurate is the method? How expensive is it? How smooth is the interpolant? How many data points are needed?
Piecewise constant interpolation

DTZ gives a comprehensive integrated property and services administration resolution for buyers, corporate house for sale In singapore owners, management firms and occupiers of property whatever their needs with the only goal of optimising and enhancing the investment worth of their property. We at the moment make use of a staff of more than 70 skilled staffs who are well-trained and dedicated to collectively achieving our purchasers' objectives.
Actual estate agency specialising in non-public condos and landed properties island vast. 10 Winstedt Highway, District 10, #01-thirteen, Singapore 227977. Property providers for enterprise relocation. Situated at 371 Beach Street, #19-10 KeyPoint, Singapore 199597. Property agents for homes, town houses, landed property, residences and condominium for sales and rentals of properties. Administration letting services for property homeowners. is there a single authority in singapore who regulates real property agents that i can file a complaint with for unethical behaviour? or is CASE is simply route? The 188 pages of Secrets and techniques of Singapore Property Gurus are full of professional knowledge and life altering wisdom. Asian industrial property market outlook Property Listing Supervisor Property Advertising Services
Should sellers go along with an agent who claims to specialize in your space? His experience might turn out to be useful, but he is probably additionally advertising a number of models within the neighbourhood – and so they're all your rivals. Within the worst-case state of affairs, your house may be used as a "showflat" as house owner YS Liang found. "Weekend after weekend, our agent would convey a stream of individuals to speed-go to our apartment, leaving within minutes. She did not even try to promote our condominium. It felt like we were just one of the many tour stops for her clients," he complains.
Step one in direction of conducting enterprise as an actual property company in Singapore is to include an organization, or if you happen to're going the partnership or sole-proprietorship route, register your Limited Legal responsibility Partnership or sole-proprietorship with the ACRA (Accounting and Company Regulatory Authority of Singapore) Whether or not you might be considering to promote, let, hire or buy a new industrial property, we're right here to assist. Search and browse our commercial property section. Possess not less than 3 years of working expertise below a Singapore licensed real-property agency; Sale, letting and property administration and taxation companies. three Shenton Means, #10-08 Shenton Home, Singapore 068805. Real property agents for purchasing, promoting, leasing, and renting property. Caveat Search
Firstly, the events might take into account to rescind the sale and buy agreement altogether. This avenue places the contracting events to a position as if the contract didn't happen. It's as if the contract was terminated from the start and events are put back into place that they were before the contract. Any items or monies handed are returned to the respective original house owners. As the worldwide real property market turns into extra refined and worldwide real property investments will increase, the ERA real estate network is well equipped to offer professional recommendation and guidance to our shoppers in making critical actual estate decisions. Relocationg, leasing and sales of properties for housing, food and beverage, retail and workplace wants.
Pasir Panjang, Singapore - $5,000-6,000 per 30 days By likelihood one among our buddies here in Singapore is an agent and we made contact for her to help us locate an residence, which she did. days from the date of execution if the doc is signed in Singapore; Be a Singapore Citizen or PR (Permanent Resident); The regulations also prohibit property agents from referring their shoppers to moneylenders, to discourage irresponsible shopping for. Brokers are additionally prohibited from holding or dealing with money on behalf of any party in relation to the sale or purchase of any property situated in Singapore, and the lease of HDB property. - Negotiate To Close A Sale together with sale and lease of HDB and private properties) Preparing your house for sale FEATURED COMMERCIAL AGENTS Property Guides
i) registered as a patent agent or its equal in any nation or territory, or by a patent workplace, specified within the Fourth Schedule; The business-specific tips for the true property agency and telecommunication sectors have been crafted to address considerations about scenarios that particularly apply to the two sectors, the PDPC stated. Mr Steven Tan, Managing Director of OrangeTee real property company, nonetheless, felt that it was a matter of "practising until it becomes part of our knowledge". "After a while, the agents ought to know the spirit behind the (Act)," he stated. Rising office sector leads real property market efficiency, while prime retail and enterprise park segments moderate and residential sector continues in decline Please choose an attendee for donation.
The simplest interpolation method is to locate the nearest data value, and assign the same value. In simple problems, this method is unlikely to be used, as linear interpolation (see below) is almost as easy, but in higher dimensional multivariate interpolation, this could be a favourable choice for its speed and simplicity.
Linear interpolation

Mining Engineer (Excluding Oil ) Truman from Alma, loves to spend time knotting, largest property developers in singapore developers in singapore and stamp collecting. Recently had a family visit to Urnes Stave Church. One of the simplest methods is linear interpolation (sometimes known as lerp). Consider the above example of estimating f(2.5). Since 2.5 is midway between 2 and 3, it is reasonable to take f(2.5) midway between f(2) = 0.9093 and f(3) = 0.1411, which yields 0.5252.
Generally, linear interpolation takes two data points, say (xa,ya) and (xb,yb), and the interpolant is given by:
Linear interpolation is quick and easy, but it is not very precise. Another disadvantage is that the interpolant is not differentiable at the point xk.
The following error estimate shows that linear interpolation is not very precise. Denote the function which we want to interpolate by g, and suppose that x lies between xa and xb and that g is twice continuously differentiable. Then the linear interpolation error is
In words, the error is proportional to the square of the distance between the data points. The error in some other methods, including polynomial interpolation and spline interpolation (described below), is proportional to higher powers of the distance between the data points. These methods also produce smoother interpolants.
Polynomial interpolation

Mining Engineer (Excluding Oil ) Truman from Alma, loves to spend time knotting, largest property developers in singapore developers in singapore and stamp collecting. Recently had a family visit to Urnes Stave Church. Polynomial interpolation is a generalization of linear interpolation. Note that the linear interpolant is a linear function. We now replace this interpolant with a polynomial of higher degree.
Consider again the problem given above. The following sixth degree polynomial goes through all the seven points:
Substituting x = 2.5, we find that f(2.5) = 0.5965.
Generally, if we have n data points, there is exactly one polynomial of degree at most n−1 going through all the data points. The interpolation error is proportional to the distance between the data points to the power n. Furthermore, the interpolant is a polynomial and thus infinitely differentiable. So, we see that polynomial interpolation overcomes most of the problems of linear interpolation.
However, polynomial interpolation also has some disadvantages. Calculating the interpolating polynomial is computationally expensive (see computational complexity) compared to linear interpolation. Furthermore, polynomial interpolation may exhibit oscillatory artifacts, especially at the end points (see Runge's phenomenon). More generally, the shape of the resulting curve, especially for very high or low values of the independent variable, may be contrary to commonsense, i.e. to what is known about the experimental system which has generated the data points. These disadvantages can be reduced by using spline interpolation or restricting attention to Chebyshev polynomials.
Spline interpolation

Mining Engineer (Excluding Oil ) Truman from Alma, loves to spend time knotting, largest property developers in singapore developers in singapore and stamp collecting. Recently had a family visit to Urnes Stave Church.
Remember that linear interpolation uses a linear function for each of intervals [xk,xk+1]. Spline interpolation uses low-degree polynomials in each of the intervals, and chooses the polynomial pieces such that they fit smoothly together. The resulting function is called a spline.
For instance, the natural cubic spline is piecewise cubic and twice continuously differentiable. Furthermore, its second derivative is zero at the end points. The natural cubic spline interpolating the points in the table above is given by
In this case we get f(2.5) = 0.5972.
Like polynomial interpolation, spline interpolation incurs a smaller error than linear interpolation and the interpolant is smoother. However, the interpolant is easier to evaluate than the high-degree polynomials used in polynomial interpolation. It also does not suffer from Runge's phenomenon. 50 year old Petroleum Engineer Kull from Dawson Creek, spends time with interests such as house brewing, property developers in singapore condo launch and camping. Discovers the beauty in planing a trip to places around the entire world, recently only coming back from .
Interpolation via Gaussian processes
Gaussian process is a powerful non-linear interpolation tool. Many popular interpolation tools are actually equivalent to particular Gaussian processes. Gaussian processes can be used not only for fitting an interpolant that passes exactly through the given data points but also for regression, i.e., for fitting a curve through noisy data. In the geostatistics community Gaussian process regression is also known as Kriging.
Other forms of interpolation
Other forms of interpolation can be constructed by picking a different class of interpolants. For instance, rational interpolation is interpolation by rational functions, and trigonometric interpolation is interpolation by trigonometric polynomials. Another possibility is to use wavelets.
The Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula can be used if the number of data points is infinite.
Multivariate interpolation is the interpolation of functions of more than one variable. Methods include bilinear interpolation and bicubic interpolation in two dimensions, and trilinear interpolation in three dimensions.
Sometimes, we know not only the value of the function that we want to interpolate, at some points, but also its derivative. This leads to Hermite interpolation problems.
When each data point is itself a function, it can be useful to see the interpolation problem as a partial advection problem between each data point. This idea leads to the displacement interpolation problem used in transportation theory.
Interpolation in digital signal processing
In the domain of digital signal processing, the term interpolation refers to the process of converting a sampled digital signal (such as a sampled audio signal) to a higher sampling rate (Upsampling) using various digital filtering techniques (e.g., convolution with a frequency-limited impulse signal). In this application there is a specific requirement that the harmonic content of the original signal be preserved without creating aliased harmonic content of the original signal above the original Nyquist limit of the signal (i.e., above fs/2 of the original signal sample rate). An early and fairly elementary discussion on this subject can be found in Rabiner and Crochiere's book Multirate Digital Signal Processing.[1]
Related concepts
The term extrapolation is used if we want to find data points outside the range of known data points.
In curve fitting problems, the constraint that the interpolant has to go exactly through the data points is relaxed. It is only required to approach the data points as closely as possible (within some other constraints). This requires parameterizing the potential interpolants and having some way of measuring the error. In the simplest case this leads to least squares approximation.
Approximation theory studies how to find the best approximation to a given function by another function from some predetermined class, and how good this approximation is. This clearly yields a bound on how well the interpolant can approximate the unknown function.
See also
Organisational Psychologist Alfonzo Lester from Timmins, enjoys pinochle, property developers in new launch singapore property and textiles. Gets motivation through travel and just spent 7 days at Alejandro de Humboldt National Park.
- Barycentric coordinates – for interpolating within on a triangle or tetrahedron
- Bilinear interpolation
- Brahmagupta's interpolation formula
- Extrapolation
- Imputation (statistics)
- Missing data
- Multivariate interpolation
- Newton–Cotes formulas
- Polynomial interpolation
- Simple rational approximation
42 year-old Environmental Consultant Merle Eure from Hudson, really loves snowboarding, property developers in new launch ec singapore and cosplay. Maintains a trip blog and has lots to write about after visiting Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (formerly Victoria Terminus).

![{\displaystyle |f(x)-g(x)|\leq C(x_{b}-x_{a})^{2}\quad {\text{where}}\quad C={\frac {1}{8}}\max _{y\in [x_{a},x_{b}]}|g''(y)|.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1d67a3bbfb850af09a3e36d5eded1d4393098cdf)

![{\displaystyle f(x)={\begin{cases}-0.1522x^{3}+0.9937x,&{\text{if }}x\in [0,1],\\-0.01258x^{3}-0.4189x^{2}+1.4126x-0.1396,&{\text{if }}x\in [1,2],\\0.1403x^{3}-1.3359x^{2}+3.2467x-1.3623,&{\text{if }}x\in [2,3],\\0.1579x^{3}-1.4945x^{2}+3.7225x-1.8381,&{\text{if }}x\in [3,4],\\0.05375x^{3}-0.2450x^{2}-1.2756x+4.8259,&{\text{if }}x\in [4,5],\\-0.1871x^{3}+3.3673x^{2}-19.3370x+34.9282,&{\text{if }}x\in [5,6].\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3cd654c9f03b663dc277263ec988f010e0d934e1)