Frequency modulation: Difference between revisions
en>ASJoshi No edit summary |
en>Dicklyon →Radio: analog is no longer "normal" for TV |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Modulation techniques}} | |||
[[File:Amfm3-en-de.gif|thumb|right|250px|A signal may be carried by an [[Amplitude modulation|AM]] or FM radio wave.|alt=Animation of audio, AM and FM signals]] | |||
In [[telecommunications]] and [[signal processing]], '''frequency modulation''' ('''FM''') is the encoding of [[information]] in a [[carrier wave]] by varying the [[instantaneous frequency]] of the wave. (Compare with [[amplitude modulation]], in which the [[amplitude]] of the carrier wave varies, while the frequency remains constant.) | |||
In [[analog signal]] applications, the difference between the instantaneous and the base frequency of the carrier is directly proportional to the instantaneous value of the input-signal amplitude. | |||
[[Digital data]] can be encoded and transmitted via a carrier wave by shifting the carrier's frequency among a predefined set of frequencies—a technique known as [[frequency-shift keying]] (FSK). FSK is widely used in [[modem]]s and [[fax modem]]s, and can also be used to send [[Morse code]].<ref>{{Cite book | |||
|title = Teach yourself electricity and electronics | |||
|author = Stan Gibilisco | |||
|publisher = McGraw-Hill Professional | |||
|year = 2002 | |||
|isbn = 978-0-07-137730-0 | |||
|page = 477 | |||
|url = http://books.google.com/?id=-Q6SBAKsmXkC&pg=PA477&dq=morse-code+frequency-shift-keying+sent-using-fsk | |||
}}</ref> [[Radioteletype]] also uses FSK.<ref>{{Cite book | |||
|title = The Electronics of Radio | |||
|author = David B. Rutledge | |||
|publisher = Cambridge University Press | |||
|year = 1999 | |||
|isbn = 978-0-521-64645-1 | |||
|page = 310 | |||
|url = http://books.google.com/?id=ZvJYLhk4N64C&pg=RA2-PA310&dq=radio-teletype+fsk | |||
}}</ref> | |||
Frequency modulation is used in [[radio]], [[telemetry]], [[radar]], seismic prospecting, and monitoring [[newborn]]s for seizures via [[EEG]].<ref>B. Boashash, editor, “Time-Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing – A Comprehensive Reference”, Elsevier Science, Oxford, 2003; ISBN 0-08-044335-4</ref> FM is widely used for [[FM broadcasting|broadcasting]] music and speech, [[two-way radio]] systems, magnetic tape-recording systems and some video-transmission systems. In radio systems, frequency modulation with sufficient [[Bandwidth (signal processing)|bandwidth]] provides an advantage in cancelling naturally-occurring noise. | |||
Frequency modulation is known as [[phase modulation]] when the carrier phase modulation is the time [[integral]] of the FM signal.{{clarify|date=July 2013}} | |||
==Theory== | |||
If the information to be transmitted (i.e., the [[baseband signal]]) is <math>x_m(t)</math> and the [[sinusoidal]] carrier is <math>x_c(t) = A_c \cos (2 \pi f_c t)\,</math>, where ''f<sub>c</sub>'' is the carrier's base frequency, and ''A<sub>c</sub>'' is the carrier's amplitude, the modulator combines the carrier with the baseband data signal to get the transmitted signal: | |||
:<math>y(t) = A_c \cos \left( 2 \pi \int_{0}^{t} f(\tau) d \tau \right)</math> | |||
::<math>= A_{c} \cos \left( 2 \pi \int_{0}^{t} \left[ f_{c} + f_{\Delta} x_{m}(\tau) \right] d \tau \right)</math> | |||
::<math> = A_{c} \cos \left( 2 \pi f_{c} t + 2 \pi f_{\Delta} \int_{0}^{t}x_{m}(\tau) d \tau \right) </math> | |||
In this equation, <math>f(\tau)\,</math> is the ''[[instantaneous phase#Instantaneous frequency|instantaneous frequency]]'' of the oscillator and <math>f_{\Delta}\,</math> is the ''[[frequency deviation]]'', which represents the maximum shift away from ''f<sub>c</sub>'' in one direction, assuming ''x''<sub>''m''</sub>(''t'') is limited to the range ±1. | |||
While most of the energy of the signal is contained within ''f<sub>c</sub>'' ± ''f''<sub>Δ</sub>, it can be shown by [[Fourier analysis]] that a wider range of frequencies is required to precisely represent an FM signal. The [[frequency spectrum]] of an actual FM signal has components extending infinitely, although their amplitude decreases and higher-order components are often neglected in practical design problems.<ref name=TGTSCS05/> | |||
===Sinusoidal baseband signal=== | |||
Mathematically, a baseband modulated signal may be approximated by a [[Sine wave|sinusoid]]al [[continuous wave]] signal with a frequency ''f<sub>m</sub>''. The integral of such a signal is: | |||
:<math>\int_{0}^{t}x_m(\tau)d \tau = \frac{A_m \cos (2 \pi f_m t)}{2 \pi f_m}\,</math> | |||
In this case, the expression for y(t) above simplifies to: | |||
:<math> y(t) = A_{c} \cos \left( 2 \pi f_{c} t + \frac{f_{\Delta}}{f_{m}} \cos \left( 2 \pi f_{m} t \right) \right)\,</math> | |||
where the amplitude <math>A_{m}\,</math> of the modulating [[Sine wave|sinusoid]] is represented by the peak deviation <math>f_{\Delta}\,</math> (see [[frequency deviation]]). | |||
The [[harmonic]] distribution of a [[sine wave]] carrier modulated by such a [[sinusoidal]] signal can be represented with [[Bessel function]]s; this provides the basis for a mathematical understanding of frequency modulation in the frequency domain. | |||
===Modulation index=== | |||
As in other modulation systems, the value of the modulation index indicates by how much the modulated variable varies around its unmodulated level. It relates to variations in the carrier frequency: | |||
:<math>h = \frac{\Delta{}f}{f_m} = \frac{f_\Delta |x_m(t)|}{f_m} \ </math> | |||
where <math>f_m\,</math> is the highest frequency component present in the modulating signal ''x''<sub>''m''</sub>(''t''), and <math>\Delta{}f\,</math> is the peak frequency-deviation—i.e. the maximum deviation of the ''[[instantaneous phase#Instantaneous frequency|instantaneous frequency]]'' from the carrier frequency. If <math>h \ll 1</math>, the modulation is called ''narrowband FM'', and its bandwidth is approximately <math>2 f_m\,</math>. | |||
If <math>h \gg 1</math>, the modulation is called ''wideband FM'' and its bandwidth is approximately <math>2 f_\Delta\,</math>. While wideband FM uses more bandwidth, it can improve the [[signal-to-noise ratio]] significantly; for example, doubling the value of <math>\Delta{}f\,</math>, while keeping <math>f_m</math> constant, results in an eight-fold improvement in the signal-to-noise ratio.<ref>Der, Lawrence, Ph.D., ''Frequency Modulation (FM) Tutorial'', http://www.silabs.com/Marcom%20Documents/Resources/FMTutorial.pdf, Silicon Laboratories, Inc., accessed 2013 February 24, p. 5</ref> (Compare this with [[Chirp spread spectrum]], which uses extremely wide frequency deviations to achieve processing gains comparable to traditional, better-known spread-spectrum modes). | |||
With a tone-modulated FM wave, if the modulation frequency is held constant and the modulation index is increased, the (non-negligible) bandwidth of the FM signal increases but the spacing between spectra remains the same; some spectral components decrease in strength as others increase. If the frequency deviation is held constant and the modulation frequency increased, the spacing between spectra increases. | |||
Frequency modulation can be classified as narrowband if the change in the carrier frequency is about the same as the signal frequency, or as wideband if the change in the carrier frequency is much higher (modulation index >1) than the signal frequency. | |||
<ref>B. P. Lathi, ''Communication Systems'', John Wiley and Sons, 1968 ISBN 0-471-51832-8, p, 214–217</ref> For example, narrowband FM is used for [[two way radio]] systems such as [[Family Radio Service]], in which the carrier is allowed to deviate only 2.5 kHz above and below the center frequency with speech signals of no more than 3.5 kHz bandwidth. Wideband FM is used for [[FM broadcasting]], in which music and speech are transmitted with up to 75 kHz deviation from the center frequency and carry audio with up to a 20-kHz bandwidth. | |||
===Bessel functions=== | |||
For the case of a carrier modulated by a single sine wave, the resulting frequency spectrum can be calculated using [[Bessel function]]s of the first kind, as a function of the sideband number and the modulation index. The carrier and sideband amplitudes are illustrated for different modulation indices of FM signals. For particular values of the modulation index, the carrier amplitude becomes zero and all the signal power is in the sidebands.<ref name=TGTSCS05>T.G. Thomas, S. C. Sekhar ''Communication Theory'', Tata-McGraw Hill 2005, ISBN 0070590915 page 136</ref> | |||
Since the sidebands are on both sides of the carrier, their count is doubled, and then multiplied by the modulating frequency to find the bandwidth. For example, 3 kHz deviation modulated by a 2.2 kHz audio tone produces a modulation index of 1.36. Examining the chart shows this modulation index will produce three sidebands. These three sidebands, when doubled, gives us (6 * 2.2 kHz) or a 13.2 kHz required bandwidth. | |||
<!-- and are spaces the width of a digit and punctuation, respectively; see [[Space (punctuation)#Table of spaces]]--> | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right;" | |||
|- | |||
!rowspan=2| Modulation<br />index | |||
!colspan=17| Sideband | |||
|- | |||
! Carrier | |||
! 1 | |||
! 2 | |||
! 3 | |||
! 4 | |||
! 5 | |||
! 6 | |||
! 7 | |||
! 8 | |||
! 9 | |||
! 10 | |||
! 11 | |||
! 12 | |||
! 13 | |||
! 14 | |||
! 15 | |||
! 16 | |||
|- | |||
! 0.00 | |||
| 1.00 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 0.25 | |||
| 0.98 | |||
| 0.12 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 0.5 | |||
| 0.94 | |||
| 0.24 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 1.0 | |||
| 0.77 | |||
| 0.44 | |||
| 0.11 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 1.5 | |||
| 0.51 | |||
| 0.56 | |||
| 0.23 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 2.0 | |||
| 0.22 | |||
| 0.58 | |||
| 0.35 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 2.41 | |||
| 0 | |||
| 0.52 | |||
| 0.43 | |||
| 0.20 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 2.5 | |||
|−0.05 | |||
| 0.50 | |||
| 0.45 | |||
| 0.22 | |||
| 0.07 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 3.0 | |||
|−0.26 | |||
| 0.34 | |||
| 0.49 | |||
| 0.31 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.04 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 4.0 | |||
|−0.40 | |||
|−0.07 | |||
| 0.36 | |||
| 0.43 | |||
| 0.28 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 5.0 | |||
|−0.18 | |||
|−0.33 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.36 | |||
| 0.39 | |||
| 0.26 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 5.53 | |||
| 0 | |||
| −0.34 | |||
| −0.13 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
| 0.40 | |||
| 0.32 | |||
| 0.19 | |||
| 0.09 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 6.0 | |||
| 0.15 | |||
|−0.28 | |||
|−0.24 | |||
| 0.11 | |||
| 0.36 | |||
| 0.36 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 7.0 | |||
| 0.30 | |||
| 0.00 | |||
|−0.30 | |||
|−0.17 | |||
| 0.16 | |||
| 0.35 | |||
| 0.34 | |||
| 0.23 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 8.0 | |||
| 0.17 | |||
| 0.23 | |||
|−0.11 | |||
|−0.29 | |||
|−0.10 | |||
| 0.19 | |||
| 0.34 | |||
| 0.32 | |||
| 0.22 | |||
| 0.13 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 8.65 | |||
| 0 | |||
| 0.27 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
|−0.24 | |||
|−0.23 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.26 | |||
| 0.34 | |||
| 0.28 | |||
| 0.18 | |||
| 0.10 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.02 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 9.0 | |||
|−0.09 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
| 0.14 | |||
|−0.18 | |||
|−0.27 | |||
|−0.06 | |||
| 0.20 | |||
| 0.33 | |||
| 0.31 | |||
| 0.21 | |||
| 0.12 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 10.0 | |||
|−0.25 | |||
| 0.04 | |||
| 0.25 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
|−0.22 | |||
|−0.23 | |||
|−0.01 | |||
| 0.22 | |||
| 0.32 | |||
| 0.29 | |||
| 0.21 | |||
| 0.12 | |||
| 0.06 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! 12.0 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
|−0.22 | |||
|−0.08 | |||
| 0.20 | |||
| 0.18 | |||
|−0.07 | |||
|−0.24 | |||
|−0.17 | |||
| 0.05 | |||
| 0.23 | |||
| 0.30 | |||
| 0.27 | |||
| 0.20 | |||
| 0.12 | |||
| 0.07 | |||
| 0.03 | |||
| 0.01 | |||
|} | |||
===Carson's rule=== | |||
{{Main|Carson bandwidth rule}} | |||
A [[rule of thumb]], ''Carson's rule'' states that nearly all (~98 percent) of the power of a frequency-modulated signal lies within a [[bandwidth (signal processing)|bandwidth]] <math> B_T\, </math> of: | |||
:<math>\ B_T = 2(\Delta f +f_m)\,</math> | |||
where <math>\Delta f\,</math>, as defined above, is the peak deviation of the instantaneous frequency <math>f(t)\,</math> from the center carrier frequency <math>f_c\,</math>. | |||
==Noise Reduction== | |||
A major advantage of FM in a communications circuit, compared for example with [[Amplitude modulation|AM]], is the possibility of improved [[Signal-to-noise ratio]] (SNR). Compared with an optimum AM scheme, FM typically has poorer SNR below a certain signal level called the noise threshold, but above a higher level – the full improvement or full quieting threshold – the SNR is much improved over AM. The improvement depends on modulation level and deviation. For typical voice communications channels, improvements are typically 5-15 dB. FM broadcasting using wider deviation can achieve even greater improvements. Additional techniques, such as pre-emphasis of higher audio frequencies with corresponding de-emphasis in the receiver, are generally used to improve overall SNR in FM circuits. Since FM signals have constant amplitude, FM receivers normally have limiters that remove AM noise, further improving SNR.<ref>{{cite book |title=Reference Data for Radio Engineers |edition=Fifth |page=21-11 |year=1970 |publisher=Howard W. Sams & Co. |editor=H. P. Westman}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=The ARRL Handbook for Radio Communications |publisher=American Radio Relay League |year=2010 |editor=H. Ward Silver and Mark J. Wilson (Eds) |author=Alan Bloom |chapter=Chapter 8. Modulation |page=8.7 |isbn=0-87259-144-8}}</ref> | |||
=={{anchor|Practical Implementation}}Implementation== | |||
===Modulation=== | |||
FM signals can be generated using either direct or indirect frequency modulation: | |||
* Direct FM modulation can be achieved by directly feeding the message into the input of a [[Voltage-controlled oscillator|VCO]]. | |||
* For indirect FM modulation, the message signal is integrated to generate a [[phase modulation|phase-modulated signal]]. This is used to modulate a [[crystal oscillator|crystal-controlled oscillator]], and the result is passed through a [[frequency multiplier]] to give an FM signal.<ref>"Communication Systems" 4th Ed, Simon Haykin, 2001</ref> | |||
===Demodulation=== | |||
{{See also|Detector_(radio)#Frequency_and_phase_modulation_detectors|l1=Detectors}} | |||
Many FM detector circuits exist. A common method for recovering the information signal is through a [[Foster-Seeley discriminator]]. A [[phase-locked loop]] can be used as an FM demodulator. ''Slope detection'' demodulates an FM signal by using a tuned circuit which has its resonant frequency slightly offset from the carrier. As the frequency rises and falls the tuned circuit provides a changing amplitude of response, converting FM to AM. AM receivers may detect some FM transmissions by this means, although it does not provide an efficient means of [[Detector (radio)|detection]] for FM broadcasts. | |||
==Applications== | |||
===Magnetic tape storage=== | |||
FM is also used at [[Intermediate frequency|intermediate frequencies]] by analog [[Video cassette recorder|VCR]] systems (including [[VHS]]) to record the [[Luminance (video)|luminance]] (black and white) portions of the video signal. Commonly, the chrominance component is recorded as a conventional AM signal, using the higher-frequency FM signal as bias. FM is the only feasible method of recording the luminance ("black and white") component of video to (and retrieving video from) [[magnetic tape]] without distortion; video signals have a large range of frequency components – from a few [[hertz]] to several [[megahertz]], too wide for [[Equalization|equalizers]] to work with due to electronic noise below −60 [[decibel|dB]]. FM also keeps the tape at saturation level, acting as a form of [[noise reduction]]; a [[audio level compression|limiter]] can mask variations in playback output, and the [[FM capture]] effect removes [[print-through]] and [[pre-echo]]. A continuous pilot-tone, if added to the signal – as was done on [[V2000]] and many Hi-band formats – can keep mechanical jitter under control and assist [[timebase correction]]. | |||
These FM systems are unusual, in that they have a ratio of carrier to maximum modulation frequency of less than two; contrast this with FM audio broadcasting, where the ratio is around 10,000. Consider, for example, a 6-MHz carrier modulated at a 3.5-MHz rate; by Bessel analysis, the first sidebands are on 9.5 and 2.5 MHz and the second sidebands are on 13 MHz and −1 MHz. The result is a reversed-phase sideband on +1 MHz; on demodulation, this results in unwanted output at 6−1 = 5 MHz. The system must be designed so that this unwanted output is reduced to an acceptable level.<ref>: "FM Systems Of Exceptional Bandwidth" Proc. IEEE vol 112, no. 9, p. 1664, September 1965</ref> | |||
===Sound=== | |||
FM is also used at [[audio frequency|audio frequencies]] to synthesize sound. This technique, known as [[frequency modulation synthesis|FM synthesis]], was popularized by early digital [[synthesizer]]s and became a standard feature in several generations of [[personal computer]] [[sound card]]s. | |||
===Radio=== | |||
[[File:FM Broadcast Transmitter High Power.jpg|200px|thumb|An American FM radio transmitter in Buffalo, NY at WEDG]] | |||
{{Main|FM broadcasting}} | |||
[[Edwin Howard Armstrong]] (1890–1954) was an American electrical engineer who invented wideband frequency modulation (FM) radio.<ref>{{Cite book | |||
|title = Principles of modern communications technology | |||
|author = A. Michael Noll | |||
|publisher = Artech House | |||
|year = 2001 | |||
|isbn = 978-1-58053-284-6 | |||
|page = 104 | |||
|url = http://books.google.com/books?id=6tDEZlwiMK0C&pg=PA104 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
He patented the regenerative circuit in 1914, the superheterodyne receiver in 1918 and the super-regenerative circuit in 1922.<ref>{{patent|US|1342885}}</ref> Armstrong presented his paper, "A Method of Reducing Disturbances in Radio Signaling by a System of Frequency Modulation", (which first described FM radio) before the New York section of the [[Institute of Radio Engineers]] on November 6, 1935. The paper was published in 1936.<ref>{{Cite journal | |||
|first = E. H. | |||
|last = Armstrong | |||
|title = A Method of Reducing Disturbances in Radio Signaling by a System of Frequency Modulation | |||
|journal = Proceedings of the IRE | |||
|volume = 24 | |||
|issue = 5 | |||
|pages = 689–740 | |||
|publisher = IRE | |||
|date= May 1936 | |||
|doi = 10.1109/JRPROC.1936.227383 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
As the name implies, wideband FM (WFM) requires a wider [[signal bandwidth]] than [[amplitude modulation]] by an equivalent modulating signal; this also makes the signal more robust against [[Noise (radio)|noise]] and [[Interference (communication)|interference]]. Frequency modulation is also more robust against signal-amplitude-fading phenomena. As a result, FM was chosen as the modulation standard for high frequency, [[high fidelity]] [[radio]] transmission, hence the term "[[FM radio]]" (although for many years the [[BBC]] called it "VHF radio" because commercial FM broadcasting uses part of the [[VHF]] band—the [[FM broadcast band]]). FM [[receiver (radio)|receivers]] employ a special [[Detector (radio)|detector]] for FM signals and exhibit a phenomenon known as the ''[[capture effect]]'', in which the [[Tuner (radio)|tuner]] "captures" the stronger of two stations on the same frequency while rejecting the other (compare this with a similar situation on an AM receiver, where both stations can be heard simultaneously). However, [[frequency drift]] or a lack of [[Electronic selectivity|selectivity]] may cause one station to be overtaken by another on an [[adjacent channel]]. Frequency [[drift (telecommunication)|drift]] was a problem in early (or inexpensive) receivers; inadequate selectivity may affect any tuner. | |||
An FM signal can also be used to carry a [[stereophonic sound|stereo]] signal; this is done with [[multiplexing]] and demultiplexing before and after the FM process. The FM modulation and demodulation process is identical in stereo and monaural processes. A high-efficiency radio-frequency [[switching amplifier]] can be used to transmit FM signals (and other [[constant envelope|constant-amplitude signals]]). For a given signal strength (measured at the receiver antenna), switching amplifiers use [[low-power electronics|less battery power]] and typically cost less than a [[linear amplifier]]. This gives FM another advantage over other modulation methods requiring linear amplifiers, such as AM and [[Quadrature amplitude modulation|QAM]]. | |||
FM is commonly used at [[VHF]] [[radio frequencies]] for [[high-fidelity]] [[radio broadcasting|broadcasts]] of music and [[Speech communication|speech]]. Analog TV sound is also broadcast using FM. Narrowband FM is used for voice communications in commercial and [[amateur radio]] settings. In broadcast services, where audio fidelity is important, wideband FM is generally used. In [[two-way radio]], narrowband FM (NBFM) is used to conserve bandwidth for land mobile, marine mobile and other radio services. | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[Amplitude modulation]] | |||
* [[Continuous-wave frequency-modulated radar]] | |||
* [[Chirp]] | |||
* [[FM broadcasting]] | |||
* [[FM stereo]] | |||
* [[FM-UWB]] (FM and Ultra Wideband) | |||
* [[History of radio]] | |||
* [[Modulation]], for a list of other modulation techniques | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|35em}} | |||
==Further reading== | |||
* A. Bruce Carlson. ''Communication Systems, 4th edition.'' McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. 2001. ISBN 0-07-011127-8, ISBN 978-0-07-011127-1. | |||
* Gary L. Frost. ''Early FM Radio: Incremental Technology in Twentieth-Century America.'' Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2010. ISBN 0-8018-9440-9, ISBN 978-0-8018-9440-4. | |||
* Ken Seymour, AT&T Wireless (Mobility). ''Frequency Modulation, The Electronics Handbook, pp 1188-1200, 1st Edition, 1996. 2nd Edition, 2005'' CRC Press, Inc., ISBN 0-8493-8345-5 (1st Edition). | |||
{{Analogue TV transmitter topics}} | |||
{{Telecommunications}} | |||
{{Audio broadcasting}} | |||
[[Category:Radio modulation modes]] | |||
Revision as of 06:10, 25 January 2014
Template:Modulation techniques
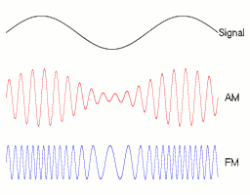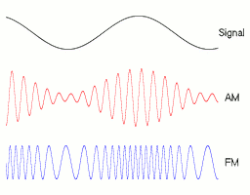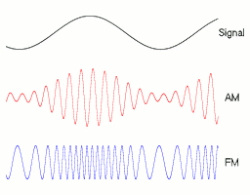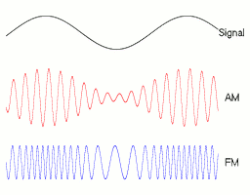
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. (Compare with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier wave varies, while the frequency remains constant.)
In analog signal applications, the difference between the instantaneous and the base frequency of the carrier is directly proportional to the instantaneous value of the input-signal amplitude.
Digital data can be encoded and transmitted via a carrier wave by shifting the carrier's frequency among a predefined set of frequencies—a technique known as frequency-shift keying (FSK). FSK is widely used in modems and fax modems, and can also be used to send Morse code.[1] Radioteletype also uses FSK.[2]
Frequency modulation is used in radio, telemetry, radar, seismic prospecting, and monitoring newborns for seizures via EEG.[3] FM is widely used for broadcasting music and speech, two-way radio systems, magnetic tape-recording systems and some video-transmission systems. In radio systems, frequency modulation with sufficient bandwidth provides an advantage in cancelling naturally-occurring noise.
Frequency modulation is known as phase modulation when the carrier phase modulation is the time integral of the FM signal.Template:Clarify
Theory
If the information to be transmitted (i.e., the baseband signal) is and the sinusoidal carrier is , where fc is the carrier's base frequency, and Ac is the carrier's amplitude, the modulator combines the carrier with the baseband data signal to get the transmitted signal:
In this equation, is the instantaneous frequency of the oscillator and is the frequency deviation, which represents the maximum shift away from fc in one direction, assuming xm(t) is limited to the range ±1.
While most of the energy of the signal is contained within fc ± fΔ, it can be shown by Fourier analysis that a wider range of frequencies is required to precisely represent an FM signal. The frequency spectrum of an actual FM signal has components extending infinitely, although their amplitude decreases and higher-order components are often neglected in practical design problems.[4]
Sinusoidal baseband signal
Mathematically, a baseband modulated signal may be approximated by a sinusoidal continuous wave signal with a frequency fm. The integral of such a signal is:
In this case, the expression for y(t) above simplifies to:
where the amplitude of the modulating sinusoid is represented by the peak deviation (see frequency deviation).
The harmonic distribution of a sine wave carrier modulated by such a sinusoidal signal can be represented with Bessel functions; this provides the basis for a mathematical understanding of frequency modulation in the frequency domain.
Modulation index
As in other modulation systems, the value of the modulation index indicates by how much the modulated variable varies around its unmodulated level. It relates to variations in the carrier frequency:
where is the highest frequency component present in the modulating signal xm(t), and is the peak frequency-deviation—i.e. the maximum deviation of the instantaneous frequency from the carrier frequency. If , the modulation is called narrowband FM, and its bandwidth is approximately .
If , the modulation is called wideband FM and its bandwidth is approximately . While wideband FM uses more bandwidth, it can improve the signal-to-noise ratio significantly; for example, doubling the value of , while keeping constant, results in an eight-fold improvement in the signal-to-noise ratio.[5] (Compare this with Chirp spread spectrum, which uses extremely wide frequency deviations to achieve processing gains comparable to traditional, better-known spread-spectrum modes).
With a tone-modulated FM wave, if the modulation frequency is held constant and the modulation index is increased, the (non-negligible) bandwidth of the FM signal increases but the spacing between spectra remains the same; some spectral components decrease in strength as others increase. If the frequency deviation is held constant and the modulation frequency increased, the spacing between spectra increases.
Frequency modulation can be classified as narrowband if the change in the carrier frequency is about the same as the signal frequency, or as wideband if the change in the carrier frequency is much higher (modulation index >1) than the signal frequency. [6] For example, narrowband FM is used for two way radio systems such as Family Radio Service, in which the carrier is allowed to deviate only 2.5 kHz above and below the center frequency with speech signals of no more than 3.5 kHz bandwidth. Wideband FM is used for FM broadcasting, in which music and speech are transmitted with up to 75 kHz deviation from the center frequency and carry audio with up to a 20-kHz bandwidth.
Bessel functions
For the case of a carrier modulated by a single sine wave, the resulting frequency spectrum can be calculated using Bessel functions of the first kind, as a function of the sideband number and the modulation index. The carrier and sideband amplitudes are illustrated for different modulation indices of FM signals. For particular values of the modulation index, the carrier amplitude becomes zero and all the signal power is in the sidebands.[4]
Since the sidebands are on both sides of the carrier, their count is doubled, and then multiplied by the modulating frequency to find the bandwidth. For example, 3 kHz deviation modulated by a 2.2 kHz audio tone produces a modulation index of 1.36. Examining the chart shows this modulation index will produce three sidebands. These three sidebands, when doubled, gives us (6 * 2.2 kHz) or a 13.2 kHz required bandwidth.
| Modulation index |
Sideband | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| 0.00 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.25 | 0.98 | 0.12 | |||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 0.94 | 0.24 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||||
| 1.0 | 0.77 | 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||
| 1.5 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| 2.0 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.03 | ||||||||||||
| 2.41 | 0 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.02 | |||||||||||
| 2.5 | −0.05 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.01 | ||||||||||
| 3.0 | −0.26 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.01 | ||||||||||
| 4.0 | −0.40 | −0.07 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.02 | |||||||||
| 5.0 | −0.18 | −0.33 | 0.05 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.02 | ||||||||
| 5.53 | 0 | −0.34 | −0.13 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |||||||
| 6.0 | 0.15 | −0.28 | −0.24 | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.02 | |||||||
| 7.0 | 0.30 | 0.00 | −0.30 | −0.17 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.02 | ||||||
| 8.0 | 0.17 | 0.23 | −0.11 | −0.29 | −0.10 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |||||
| 8.65 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.06 | −0.24 | −0.23 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.02 | ||||
| 9.0 | −0.09 | 0.25 | 0.14 | −0.18 | −0.27 | −0.06 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |||
| 10.0 | −0.25 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.06 | −0.22 | −0.23 | −0.01 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.01 | ||
| 12.0 | 0.05 | −0.22 | −0.08 | 0.20 | 0.18 | −0.07 | −0.24 | −0.17 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
Carson's rule
Mining Engineer (Excluding Oil ) Truman from Alma, loves to spend time knotting, largest property developers in singapore developers in singapore and stamp collecting. Recently had a family visit to Urnes Stave Church.
A rule of thumb, Carson's rule states that nearly all (~98 percent) of the power of a frequency-modulated signal lies within a bandwidth of:
where , as defined above, is the peak deviation of the instantaneous frequency from the center carrier frequency .
Noise Reduction
A major advantage of FM in a communications circuit, compared for example with AM, is the possibility of improved Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Compared with an optimum AM scheme, FM typically has poorer SNR below a certain signal level called the noise threshold, but above a higher level – the full improvement or full quieting threshold – the SNR is much improved over AM. The improvement depends on modulation level and deviation. For typical voice communications channels, improvements are typically 5-15 dB. FM broadcasting using wider deviation can achieve even greater improvements. Additional techniques, such as pre-emphasis of higher audio frequencies with corresponding de-emphasis in the receiver, are generally used to improve overall SNR in FM circuits. Since FM signals have constant amplitude, FM receivers normally have limiters that remove AM noise, further improving SNR.[7][8]
<Practical Implementation>...</Practical Implementation>Implementation
Modulation
FM signals can be generated using either direct or indirect frequency modulation:
- Direct FM modulation can be achieved by directly feeding the message into the input of a VCO.
- For indirect FM modulation, the message signal is integrated to generate a phase-modulated signal. This is used to modulate a crystal-controlled oscillator, and the result is passed through a frequency multiplier to give an FM signal.[9]
Demodulation
DTZ's public sale group in Singapore auctions all forms of residential, workplace and retail properties, outlets, homes, lodges, boarding homes, industrial buildings and development websites. Auctions are at present held as soon as a month.
We will not only get you a property at a rock-backside price but also in an space that you've got longed for. You simply must chill out back after giving us the accountability. We will assure you 100% satisfaction. Since we now have been working in the Singapore actual property market for a very long time, we know the place you may get the best property at the right price. You will also be extremely benefited by choosing us, as we may even let you know about the precise time to invest in the Singapore actual property market.
The Hexacube is offering new ec launch singapore business property for sale Singapore investors want to contemplate. Residents of the realm will likely appreciate that they'll customize the business area that they wish to purchase as properly. This venture represents one of the crucial expansive buildings offered in Singapore up to now. Many investors will possible want to try how they will customise the property that they do determine to buy by means of here. This location has offered folks the prospect that they should understand extra about how this course of can work as well.
Singapore has been beckoning to traders ever since the value of properties in Singapore started sky rocketing just a few years again. Many businesses have their places of work in Singapore and prefer to own their own workplace area within the country once they decide to have a everlasting office. Rentals in Singapore in the corporate sector can make sense for some time until a business has discovered a agency footing. Finding Commercial Property Singapore takes a variety of time and effort but might be very rewarding in the long term.
is changing into a rising pattern among Singaporeans as the standard of living is increasing over time and more Singaporeans have abundance of capital to invest on properties. Investing in the personal properties in Singapore I would like to applaud you for arising with such a book which covers the secrets and techniques and tips of among the profitable Singapore property buyers. I believe many novice investors will profit quite a bit from studying and making use of some of the tips shared by the gurus." – Woo Chee Hoe Special bonus for consumers of Secrets of Singapore Property Gurus Actually, I can't consider one other resource on the market that teaches you all the points above about Singapore property at such a low value. Can you? Condominium For Sale (D09) – Yong An Park For Lease
In 12 months 2013, c ommercial retails, shoebox residences and mass market properties continued to be the celebrities of the property market. Models are snapped up in report time and at document breaking prices. Builders are having fun with overwhelming demand and patrons need more. We feel that these segments of the property market are booming is a repercussion of the property cooling measures no.6 and no. 7. With additional buyer's stamp responsibility imposed on residential properties, buyers change their focus to commercial and industrial properties. I imagine every property purchasers need their property funding to understand in value.
Many FM detector circuits exist. A common method for recovering the information signal is through a Foster-Seeley discriminator. A phase-locked loop can be used as an FM demodulator. Slope detection demodulates an FM signal by using a tuned circuit which has its resonant frequency slightly offset from the carrier. As the frequency rises and falls the tuned circuit provides a changing amplitude of response, converting FM to AM. AM receivers may detect some FM transmissions by this means, although it does not provide an efficient means of detection for FM broadcasts.
Applications
Magnetic tape storage
FM is also used at intermediate frequencies by analog VCR systems (including VHS) to record the luminance (black and white) portions of the video signal. Commonly, the chrominance component is recorded as a conventional AM signal, using the higher-frequency FM signal as bias. FM is the only feasible method of recording the luminance ("black and white") component of video to (and retrieving video from) magnetic tape without distortion; video signals have a large range of frequency components – from a few hertz to several megahertz, too wide for equalizers to work with due to electronic noise below −60 dB. FM also keeps the tape at saturation level, acting as a form of noise reduction; a limiter can mask variations in playback output, and the FM capture effect removes print-through and pre-echo. A continuous pilot-tone, if added to the signal – as was done on V2000 and many Hi-band formats – can keep mechanical jitter under control and assist timebase correction.
These FM systems are unusual, in that they have a ratio of carrier to maximum modulation frequency of less than two; contrast this with FM audio broadcasting, where the ratio is around 10,000. Consider, for example, a 6-MHz carrier modulated at a 3.5-MHz rate; by Bessel analysis, the first sidebands are on 9.5 and 2.5 MHz and the second sidebands are on 13 MHz and −1 MHz. The result is a reversed-phase sideband on +1 MHz; on demodulation, this results in unwanted output at 6−1 = 5 MHz. The system must be designed so that this unwanted output is reduced to an acceptable level.[10]
Sound
FM is also used at audio frequencies to synthesize sound. This technique, known as FM synthesis, was popularized by early digital synthesizers and became a standard feature in several generations of personal computer sound cards.
Radio

Mining Engineer (Excluding Oil ) Truman from Alma, loves to spend time knotting, largest property developers in singapore developers in singapore and stamp collecting. Recently had a family visit to Urnes Stave Church. Edwin Howard Armstrong (1890–1954) was an American electrical engineer who invented wideband frequency modulation (FM) radio.[11] He patented the regenerative circuit in 1914, the superheterodyne receiver in 1918 and the super-regenerative circuit in 1922.[12] Armstrong presented his paper, "A Method of Reducing Disturbances in Radio Signaling by a System of Frequency Modulation", (which first described FM radio) before the New York section of the Institute of Radio Engineers on November 6, 1935. The paper was published in 1936.[13]
As the name implies, wideband FM (WFM) requires a wider signal bandwidth than amplitude modulation by an equivalent modulating signal; this also makes the signal more robust against noise and interference. Frequency modulation is also more robust against signal-amplitude-fading phenomena. As a result, FM was chosen as the modulation standard for high frequency, high fidelity radio transmission, hence the term "FM radio" (although for many years the BBC called it "VHF radio" because commercial FM broadcasting uses part of the VHF band—the FM broadcast band). FM receivers employ a special detector for FM signals and exhibit a phenomenon known as the capture effect, in which the tuner "captures" the stronger of two stations on the same frequency while rejecting the other (compare this with a similar situation on an AM receiver, where both stations can be heard simultaneously). However, frequency drift or a lack of selectivity may cause one station to be overtaken by another on an adjacent channel. Frequency drift was a problem in early (or inexpensive) receivers; inadequate selectivity may affect any tuner.
An FM signal can also be used to carry a stereo signal; this is done with multiplexing and demultiplexing before and after the FM process. The FM modulation and demodulation process is identical in stereo and monaural processes. A high-efficiency radio-frequency switching amplifier can be used to transmit FM signals (and other constant-amplitude signals). For a given signal strength (measured at the receiver antenna), switching amplifiers use less battery power and typically cost less than a linear amplifier. This gives FM another advantage over other modulation methods requiring linear amplifiers, such as AM and QAM.
FM is commonly used at VHF radio frequencies for high-fidelity broadcasts of music and speech. Analog TV sound is also broadcast using FM. Narrowband FM is used for voice communications in commercial and amateur radio settings. In broadcast services, where audio fidelity is important, wideband FM is generally used. In two-way radio, narrowband FM (NBFM) is used to conserve bandwidth for land mobile, marine mobile and other radio services.
See also
- Amplitude modulation
- Continuous-wave frequency-modulated radar
- Chirp
- FM broadcasting
- FM stereo
- FM-UWB (FM and Ultra Wideband)
- History of radio
- Modulation, for a list of other modulation techniques
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
Further reading
- A. Bruce Carlson. Communication Systems, 4th edition. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. 2001. ISBN 0-07-011127-8, ISBN 978-0-07-011127-1.
- Gary L. Frost. Early FM Radio: Incremental Technology in Twentieth-Century America. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2010. ISBN 0-8018-9440-9, ISBN 978-0-8018-9440-4.
- Ken Seymour, AT&T Wireless (Mobility). Frequency Modulation, The Electronics Handbook, pp 1188-1200, 1st Edition, 1996. 2nd Edition, 2005 CRC Press, Inc., ISBN 0-8493-8345-5 (1st Edition).
Template:Analogue TV transmitter topics Template:Telecommunications Template:Audio broadcasting
- ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ B. Boashash, editor, “Time-Frequency Signal Analysis and Processing – A Comprehensive Reference”, Elsevier Science, Oxford, 2003; ISBN 0-08-044335-4
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 T.G. Thomas, S. C. Sekhar Communication Theory, Tata-McGraw Hill 2005, ISBN 0070590915 page 136
- ↑ Der, Lawrence, Ph.D., Frequency Modulation (FM) Tutorial, http://www.silabs.com/Marcom%20Documents/Resources/FMTutorial.pdf, Silicon Laboratories, Inc., accessed 2013 February 24, p. 5
- ↑ B. P. Lathi, Communication Systems, John Wiley and Sons, 1968 ISBN 0-471-51832-8, p, 214–217
- ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ "Communication Systems" 4th Ed, Simon Haykin, 2001
- ↑ : "FM Systems Of Exceptional Bandwidth" Proc. IEEE vol 112, no. 9, p. 1664, September 1965
- ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ Template:Patent
- ↑ One of the biggest reasons investing in a Singapore new launch is an effective things is as a result of it is doable to be lent massive quantities of money at very low interest rates that you should utilize to purchase it. Then, if property values continue to go up, then you'll get a really high return on funding (ROI). Simply make sure you purchase one of the higher properties, reminiscent of the ones at Fernvale the Riverbank or any Singapore landed property Get Earnings by means of Renting
In its statement, the singapore property listing - website link, government claimed that the majority citizens buying their first residence won't be hurt by the new measures. Some concessions can even be prolonged to chose teams of consumers, similar to married couples with a minimum of one Singaporean partner who are purchasing their second property so long as they intend to promote their first residential property. Lower the LTV limit on housing loans granted by monetary establishments regulated by MAS from 70% to 60% for property purchasers who are individuals with a number of outstanding housing loans on the time of the brand new housing purchase. Singapore Property Measures - 30 August 2010 The most popular seek for the number of bedrooms in Singapore is 4, followed by 2 and three. Lush Acres EC @ Sengkang
Discover out more about real estate funding in the area, together with info on international funding incentives and property possession. Many Singaporeans have been investing in property across the causeway in recent years, attracted by comparatively low prices. However, those who need to exit their investments quickly are likely to face significant challenges when trying to sell their property – and could finally be stuck with a property they can't sell. Career improvement programmes, in-house valuation, auctions and administrative help, venture advertising and marketing, skilled talks and traisning are continuously planned for the sales associates to help them obtain better outcomes for his or her shoppers while at Knight Frank Singapore. No change Present Rules
Extending the tax exemption would help. The exemption, which may be as a lot as $2 million per family, covers individuals who negotiate a principal reduction on their existing mortgage, sell their house short (i.e., for lower than the excellent loans), or take part in a foreclosure course of. An extension of theexemption would seem like a common-sense means to assist stabilize the housing market, but the political turmoil around the fiscal-cliff negotiations means widespread sense could not win out. Home Minority Chief Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) believes that the mortgage relief provision will be on the table during the grand-cut price talks, in response to communications director Nadeam Elshami. Buying or promoting of blue mild bulbs is unlawful.
A vendor's stamp duty has been launched on industrial property for the primary time, at rates ranging from 5 per cent to 15 per cent. The Authorities might be trying to reassure the market that they aren't in opposition to foreigners and PRs investing in Singapore's property market. They imposed these measures because of extenuating components available in the market." The sale of new dual-key EC models will even be restricted to multi-generational households only. The models have two separate entrances, permitting grandparents, for example, to dwell separately. The vendor's stamp obligation takes effect right this moment and applies to industrial property and plots which might be offered inside three years of the date of buy. JLL named Best Performing Property Brand for second year running
The data offered is for normal info purposes only and isn't supposed to be personalised investment or monetary advice. Motley Fool Singapore contributor Stanley Lim would not personal shares in any corporations talked about. Singapore private home costs increased by 1.eight% within the fourth quarter of 2012, up from 0.6% within the earlier quarter. Resale prices of government-built HDB residences which are usually bought by Singaporeans, elevated by 2.5%, quarter on quarter, the quickest acquire in five quarters. And industrial property, prices are actually double the levels of three years ago. No withholding tax in the event you sell your property. All your local information regarding vital HDB policies, condominium launches, land growth, commercial property and more
There are various methods to go about discovering the precise property. Some local newspapers (together with the Straits Instances ) have categorised property sections and many local property brokers have websites. Now there are some specifics to consider when buying a 'new launch' rental. Intended use of the unit Every sale begins with 10 p.c low cost for finish of season sale; changes to 20 % discount storewide; follows by additional reduction of fiftyand ends with last discount of 70 % or extra. Typically there is even a warehouse sale or transferring out sale with huge mark-down of costs for stock clearance. Deborah Regulation from Expat Realtor shares her property market update, plus prime rental residences and houses at the moment available to lease Esparina EC @ Sengkang



![{\displaystyle =A_{c}\cos \left(2\pi \int _{0}^{t}\left[f_{c}+f_{\Delta }x_{m}(\tau )\right]d\tau \right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/00bbc8788a88c6b7d313c7586dbfc5efd8c7aa27)


















