Work (physics): Difference between revisions
en>EmausBot m r2.7.2+) (Robot: Modifying ca:Treball (física) |
en>ClueBot NG m Reverting possible vandalism by Bmull96 to version by 184.97.209.101. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (1683304) (Bot) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:wiener process zoom.png|thumb|300px|A single realization of a one-dimensional Wiener process]] | |||
[[Image:Wiener process 3d.png|thumb|300px|A single realization of a three-dimensional Wiener process]] | |||
In [[mathematics]], the '''Wiener process''' is a continuous-time [[stochastic process]] named in honor of [[Norbert Wiener]]. It is often called standard '''[[Brownian motion]]''', after [[Robert Brown (botanist)|Robert Brown]]. It is one of the best known [[Lévy process]]es ([[càdlàg]] stochastic processes with [[stationary process|stationary]] [[statistical independence|independent]] increments) and occurs frequently in pure and applied mathematics, [[economy|economics]], quantitative finance and [[physics]]. | |||
The Wiener process plays an important role both in pure and applied mathematics. In pure mathematics, the Wiener process gave rise to the study of continuous time [[martingale (probability theory)|martingale]]s. It is a key process in terms of which more complicated stochastic processes can be described. As such, it plays a vital role in [[stochastic calculus]], [[diffusion process]]es and even [[potential theory]]. It is the driving process of [[Schramm–Loewner evolution]]. In [[applied mathematics]], the Wiener process is used to represent the integral of a [[Gaussian distribution|Gaussian]] [[white noise]] process, and so is useful as a model of noise in [[electronics engineering]], instrument errors in [[Filter (signal processing)|filtering theory]] and unknown forces in [[control theory]]. | |||
The Wiener process has applications throughout the mathematical sciences. In physics it is used to study [[Brownian motion]], the diffusion of minute particles suspended in fluid, and other types of [[diffusion]] via the [[Fokker–Planck equation|Fokker–Planck]] and [[Langevin equation]]s. It also forms the basis for the rigorous [[path integral formulation]] of [[quantum mechanics]] (by the [[Feynman–Kac formula]], a solution to the [[Schrödinger equation]] can be represented in terms of the Wiener process) and the study of [[eternal inflation]] in [[physical cosmology]]. It is also prominent in the [[mathematical finance|mathematical theory of finance]], in particular the [[Black–Scholes]] option pricing model. | |||
==Characterizations of the Wiener process== | |||
The Wiener process ''W<sub>t</sub>'' is characterized by three properties:<ref>Durrett 1996, Sect. 7.1</ref> | |||
#''W''<sub>0</sub> = 0 | |||
# The function ''t'' → ''W<sub>t</sub>'' is [[almost surely]] everywhere continuous | |||
#''W<sub>t</sub>'' has independent increments with ''W<sub>t</sub>''−''W<sub>s</sub>'' ~ ''N''(0, ''t''−''s'') (for 0 ≤ ''s'' < ''t''), where ''N''(μ, σ<sup>2</sup>) denotes the [[normal distribution]] with [[expected value]] μ and [[variance]] σ<sup>2</sup>. | |||
The last condition means that if 0 ≤ ''s''<sub>1</sub> < ''t''<sub>1</sub> ≤ ''s''<sub>2</sub> < ''t''<sub>2</sub> then ''W''<sub>''t''<sub>1</sub></sub>−''W''<sub>''s''<sub>1</sub></sub> and ''W''<sub>''t''<sub>2</sub></sub>−''W''<sub>''s''<sub>2</sub></sub> are independent random variables, and the similar condition holds for ''n'' increments. | |||
An alternative characterization of the Wiener process is the so-called ''Lévy characterization'' that says that the Wiener process is an almost surely continuous [[martingale (probability theory)|martingale]] with ''W''<sub>0</sub> = 0 and [[quadratic variation]] [''W''<sub>''t''</sub>, ''W''<sub>''t''</sub>] = ''t'' (which means that ''W''<sub>''t''</sub><sup>2</sup>−''t'' is also a martingale). | |||
A third characterization is that the Wiener process has a spectral representation as a sine series whose coefficients are independent ''N''(0, 1) random variables. This representation can be obtained using the [[Karhunen–Loève theorem]]. | |||
Another characterization of a Wiener process is the [[Definite integral]] (from zero to time t) of a zero mean, unit variance, delta correlated ("white") [[Gaussian process]]. | |||
The Wiener process can be constructed as the [[scaling limit]] of a [[random walk]], or other discrete-time stochastic processes with stationary independent increments. This is known as [[Donsker's theorem]]. Like the random walk, the Wiener process is recurrent in one or two dimensions (meaning that it returns almost surely to any fixed [[neighborhood (mathematics)|neighborhood]] of the origin infinitely often) whereas it is not recurrent in dimensions three and higher{{citation needed|date=April 2013}}. Unlike the random walk, it is [[scale invariance|scale invariant]], meaning that | |||
:<math>\alpha^{-1}W_{\alpha^2 t}</math> | |||
is a Wiener process for any nonzero constant α. The '''Wiener measure''' is the [[Law (stochastic processes)|probability law]] on the space of [[continuous function]]s ''g'', with ''g''(0) = 0, induced by the Wiener process. An [[integral]] based on Wiener measure may be called a '''Wiener integral'''. | |||
==Properties of a one-dimensional Wiener process== | |||
===Basic properties=== | |||
The unconditional [[probability density function]] at a fixed time ''t'': | |||
:<math>f_{W_t}(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi t}} e^{-\frac{x^2}{2t}}.</math> | |||
The [[expected value|expectation]] is zero: | |||
:<math>E[W_t] = 0.</math> | |||
The [[variance]], using the [[Computational formula for the variance|computational formula]], is ''t'': | |||
:<math>\operatorname{Var}(W_t) =E\left[W^2_t \right ] - E^2[W_t] = E \left [W^2_t \right] - 0 = E \left [W^2_t \right ] = t.</math> | |||
The [[covariance function|covariance]] and [[correlation function|correlation]]: | |||
:<math>\operatorname{cov}(W_s,W_t) = \min(s,t),</math> | |||
:<math>\operatorname{corr}(W_s,W_t) = \frac{\mathrm{cov}(W_s,W_t)}{\sigma_{W_s} \sigma_{W_t}} = \frac{\min(s,t)}{\sqrt{st}} =\sqrt{\frac{\min(s,t)}{\max(s,t)}}.</math> | |||
The results for the expectation and variance follow immediately from the definition that increments have a [[normal distribution]], centered at zero. Thus | |||
:<math>W_t = W_t-W_0 \sim N(0,t).</math> | |||
The results for the covariance and correlation follow from the definition that non-overlapping increments are independent, of which only the property that they are uncorrelated is used. Suppose that ''t''<sub>1</sub> < ''t''<sub>2</sub>. | |||
:<math>\operatorname{cov}(W_{t_1}, W_{t_2}) = E\left[(W_{t_1}-E[W_{t_1}]) \cdot (W_{t_2}-E[W_{t_2}])\right] = E\left[W_{t_1} \cdot W_{t_2} \right].</math> | |||
Substituting | |||
:<math> W_{t_2} = ( W_{t_2} - W_{t_1} ) + W_{t_1} </math> | |||
we arrive at: | |||
:<math>E[W_{t_1} \cdot W_{t_2}] = E\left[W_{t_1} \cdot ((W_{t_2} - W_{t_1})+ W_{t_1}) \right] = E\left[W_{t_1} \cdot (W_{t_2} - W_{t_1} )\right] + E\left [W_{t_1}^2 \right].</math> | |||
Since ''W''(''t''<sub>1</sub>) = ''W''(''t''<sub>1</sub>)−''W''(''t''<sub>0</sub>) and ''W''(''t''<sub>2</sub>)−''W''(''t''<sub>1</sub>), are independent, | |||
:<math> E\left [W_{t_1} \cdot (W_{t_2} - W_{t_1} ) \right ] = E[W_{t_1}] \cdot E[W_{t_2} - W_{t_1}] = 0.</math> | |||
Thus | |||
:<math>\operatorname{cov}(W_{t_1}, W_{t_2}) = E \left [W_{t_1}^2 \right ] = t_1.</math> | |||
=== Wiener representation=== | |||
Wiener (1923) also gave a representation of a Brownian path in terms of a random [[Fourier series]]. If <math>\xi_n</math> are independent Gaussian variables with mean zero and variance one, then | |||
:<math>W_t=\xi_0 t+ \sqrt{2}\sum_{n=1}\xi_n\frac{\sin \pi n t}{\pi n}</math> | |||
and | |||
:<math> W_t = \sqrt{2} \sum_{n=1}^\infty \xi_n \frac{\sin \left(\left(n - \frac{1}{2}\right) \pi t\right)}{ \left(n - \frac{1}{2}\right) \pi} </math> | |||
represent a Brownian motion on <math>[0,1]</math>. The scaled process | |||
:<math>\sqrt{c}\, W\left(\frac{t}{c}\right)</math> | |||
is a Brownian motion on <math>[0,c]</math> (cf. [[Karhunen–Loève theorem]]). | |||
=== Running maximum === | |||
The joint distribution of the running maximum | |||
:<math> M_t = \max_{0 \leq s \leq t} W_s </math> | |||
and ''W<sub>t</sub>'' is | |||
: <math> f_{M_t,W_t}(m,w) = \frac{2(2m - w)}{t\sqrt{2 \pi t}} e^{-\frac{(2m-w)^2}{2t}}, \qquad m \ge 0, w \leq m.</math> | |||
To get the unconditional distribution of <math>f_{M_t}</math>, integrate over −∞ < ''w'' ≤ ''m'' : | |||
<math> f_{M_t}(m) = \int_{-\infty}^{m} f_{M_t,W_t}(m,w)\,dw = \int_{-\infty}^{m} \frac{2(2m - w)}{t\sqrt{2 \pi t}} e^{-\frac{(2m-w)^2}{2t}}\,dw = \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi t}}e^{-\frac{m^2}{2t}}</math> | |||
And the expectation<ref>{{cite book|last=Shreve|first=Steven E|title=Stochastic Calculus for Finance II: Continuous Time Models|year=2008|publisher=Springer|isbn=978-0-387-40101-0|pages=114}}</ref> | |||
: <math> E[M_t] = \int_{0}^{\infty} m f_{M_t}(m)\,dm = \int_{0}^{\infty} m \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi t}}e^{-\frac{m^2}{2t}}\,dm = \sqrt{\frac{2t}{\pi}} </math> | |||
=== Self-similarity === | |||
[[Image:Wiener process animated.gif|thumb|500px|A demonstration of Brownian scaling, showing <math>V_t = (1/\sqrt c) W_{ct}</math> for decreasing ''c''. Note that the average features of the function do not change while zooming in, and note that it zooms in quadratically faster horizontally than vertically. <!-- Feel free to rewrite this... -->]] | |||
==== Brownian scaling ==== | |||
For every ''c'' > 0 the process <math> V_t = (1/\sqrt c) W_{ct} </math> is another Wiener process. | |||
==== Time reversal ==== | |||
The process <math> V_t = W_1 - W_{1-t} </math> for 0 ≤ ''t'' ≤ 1 is distributed like ''W<sub>t</sub>'' for 0 ≤ ''t'' ≤ 1. | |||
==== Time inversion ==== | |||
The process <math> V_t = t W_{1/t} </math> is another Wiener process. | |||
=== A class of Brownian martingales === | |||
If a [[polynomial]] ''p''(''x'', ''t'') satisfies the [[Partial differential equation|PDE]] | |||
: <math>\left( \frac{\partial}{\partial t} + \frac{1}{2} \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} \right) p(x,t) = 0 </math> | |||
then the stochastic process | |||
: <math> M_t = p ( W_t, t )</math> | |||
is a [[martingale (probability theory)|martingale]]. | |||
'''Example:''' <math> W_t^2 - t </math> is a martingale, which shows that the [[quadratic variation]] of ''W'' on [0, ''t''] is equal to ''t''. It follows that the expected [[first exit time|time of first exit]] of ''W'' from (−''c'', ''c'') is equal to ''c''<sup>2</sup>. | |||
More generally, for every polynomial ''p''(''x'', ''t'') the following stochastic process is a martingale: | |||
: <math> M_t = p ( W_t, t ) - \int_0^t a(W_s,s) \, \mathrm{d}s, </math> | |||
where ''a'' is the polynomial | |||
: <math> a(x,t) = \left( \frac{\partial}{\partial t} + \frac12 \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} \right) p(x,t). </math> | |||
'''Example:''' <math> p(x,t) = (x^2-t)^2, </math> <math> a(x,t) = 4x^2; </math> the process | |||
:<math> (W_t^2 - t)^2 - 4 \int_0^t W_s^2 \, \mathrm{d}s </math> | |||
is a martingale, which shows that the quadratic variation of the martingale <math> W_t^2 - t </math> on [0, ''t''] is equal to | |||
:<math> 4 \int_0^t W_s^2 \, \mathrm{d}s.</math> | |||
About functions ''p''(''xa'', ''t'') more general than polynomials, see [[Local martingale#Martingales via local martingales|local martingales]]. | |||
=== Some properties of sample paths === | |||
The set of all functions ''w'' with these properties is of full Wiener measure. That is, a path (sample function) of the Wiener process has all these properties almost surely. | |||
==== Qualitative properties ==== | |||
* For every ε > 0, the function ''w'' takes both (strictly) positive and (strictly) negative values on (0, ε). | |||
* The function ''w'' is continuous everywhere but differentiable nowhere (like the [[Weierstrass function]]). | |||
* Points of [[Maxima and minima|local maximum]] of the function ''w'' are a dense countable set; the maximum values are pairwise different; each local maximum is sharp in the following sense: if ''w'' has a local maximum at ''t'' then | |||
::<math>\lim_{s \to t} \frac{|w(s)-w(t)|}{|s-t|} \to \infty.</math> | |||
:The same holds for local minima. | |||
* The function ''w'' has no points of local increase, that is, no ''t'' > 0 satisfies the following for some ε in (0, ''t''): first, ''w''(''s'') ≤ ''w''(''t'') for all ''s'' in (''t'' − ε, ''t''), and second, ''w''(''s'') ≥ ''w''(''t'') for all ''s'' in (''t'', ''t'' + ε). (Local increase is a weaker condition than that ''w'' is increasing on (''t'' − ε, ''t'' + ε).) The same holds for local decrease. | |||
* The function ''w'' is of [[bounded variation|unbounded variation]] on every interval. | |||
* [[root of a function|Zeros]] of the function ''w'' are a [[nowhere dense set|nowhere dense]] [[perfect set]] of Lebesgue measure 0 and [[Hausdorff dimension]] 1/2 (therefore, uncountable). | |||
==== Quantitative properties ==== | |||
===== [[Law of the iterated logarithm]] ===== | |||
: <math> \limsup_{t\to+\infty} \frac{ |w(t)| }{ \sqrt{ 2t \log\log t } } = 1, \quad \text{almost surely}. </math> | |||
===== [[Modulus of continuity]] ===== | |||
Local modulus of continuity: | |||
: <math> \limsup_{\varepsilon\to0+} \frac{ |w(\varepsilon)| }{ \sqrt{ 2\varepsilon \log\log(1/\varepsilon) } } = 1, \qquad \text{almost surely}. </math> | |||
[[Lévy's modulus of continuity theorem|Global modulus of continuity]] (Lévy): | |||
: <math> \limsup_{\varepsilon\to0+} \sup_{0\le s<t\le 1, t-s\le\varepsilon}\frac{|w(s)-w(t)|}{\sqrt{ 2\varepsilon \log(1/\varepsilon)}} = 1, \qquad \text{almost surely}. </math> | |||
==== Local time ==== | |||
The image of the [[Lebesgue measure]] on [0, ''t''] under the map ''w'' (the [[pushforward measure]]) has a density ''L''<sub>''t''</sub>(·). Thus, | |||
: <math> \int_0^t f(w(s)) \, \mathrm{d}s = \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} f(x) L_t(x) \, \mathrm{d}x </math> | |||
for a wide class of functions ''f'' (namely: all continuous functions; all locally integrable functions; all non-negative measurable functions). The density ''L<sub>t</sub>'' is (more exactly, can and will be chosen to be) continuous. The number ''L<sub>t</sub>''(''x'') is called the [[local time (mathematics)|local time]] at ''x'' of ''w'' on [0, ''t'']. It is strictly positive for all ''x'' of the interval (''a'', ''b'') where ''a'' and ''b'' are the least and the greatest value of ''w'' on [0, ''t''], respectively. (For ''x'' outside this interval the local time evidently vanishes.) Treated as a function of two variables ''x'' and ''t'', the local time is still continuous. Treated as a function of ''t'' (while ''x'' is fixed), the local time is a [[singular function]] corresponding to a [[atom (measure theory)|nonatomic]] measure on the set of zeros of ''w''. | |||
These continuity properties are fairly non-trivial. Consider that the local time can also be defined (as the density of the pushforward measure) for a smooth function. Then, however, the density is discontinuous, unless the given function is monotone. In other words, there is a conflict between good behavior of a function and good behavior of its local time. In this sense, the continuity of the local time of the Wiener process is another manifestation of non-smoothness of the trajectory. | |||
==Related processes== | |||
[[Image:BMonSphere.jpg|thumb|The generator of a Brownian motion is ½ times the [[Laplace–Beltrami operator]]. The image above is of the Brownian motion on a special manifold: the surface of a sphere.]] | |||
The stochastic process defined by | |||
:<math> X_t = \mu t + \sigma W_t</math> | |||
is called a '''Wiener process with drift μ''' and infinitesimal variance σ<sup>2</sub>. These processes exhaust continuous [[Lévy process]]es. | |||
Two random processes on the time interval [0, 1] appear, roughly speaking, when conditioning the Wiener process to vanish on both ends of [0,1]. With no further conditioning, the process takes both positive and negative values on [0, 1] and is called [[Brownian bridge]]. Conditioned also to stay positive on (0, 1), the process is called [[Brownian excursion]].<ref>{{cite journal |last=Vervaat |first=W. |year=1979 |title=A relation between Brownian bridge and Brownian excursion |journal=[[Annals of Probability]] |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=143–149 |jstor=2242845 }}</ref> In both cases a rigorous treatment involves a limiting procedure, since the formula ''P''(''A''|''B'') = ''P''(''A'' ∩ ''B'')/''P''(''B'') does not apply when ''P''(''B'') = 0. | |||
A [[geometric Brownian motion]] can be written | |||
:<math> e^{\mu t-\frac{\sigma^2 t}{2}+\sigma W_t}.</math> | |||
It is a stochastic process which is used to model processes that can never take on negative values, such as the value of stocks. | |||
The stochastic process | |||
:<math>X_t = e^{-t} W_{e^{2t}}</math> | |||
is distributed like the [[Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process]]. | |||
The [[hitting time|time of hitting]] a single point ''x'' > 0 by the Wiener process is a random variable with the [[Lévy distribution]]. The family of these random variables (indexed by all positive numbers ''x'') is a [[left-continuous]] modification of a [[Lévy process]]. The [[right-continuous]] [[random process|modification]] of this process is given by times of [[hitting time|first exit]] from closed intervals [0, ''x'']. | |||
The [[Local time (mathematics)|local time]] ''L'' = (''L<sup>x</sup><sub>t</sub>'')<sub>''x'' ∈ '''R''', ''t'' ≥ 0</sub> of a Brownian motion describes the time that the process spends at the point ''x''. Formally | |||
:<math>L^x(t) =\int_0^t \delta(x-B_t)\,ds</math> | |||
where δ is the [[Dirac delta function]]. The behaviour of the local time is characterised by [[Local time (mathematics)#Ray-Knight Theorems|Ray–Knight theorems]]. | |||
=== Brownian martingales === | |||
Let ''A'' be an event related to the Wiener process (more formally: a set, measurable with respect to the Wiener measure, in the space of functions), and ''X<sub>t</sub>'' the conditional probability of ''A'' given the Wiener process on the time interval [0, ''t''] (more formally: the Wiener measure of the set of trajectories whose concatenation with the given partial trajectory on [0, ''t''] belongs to ''A''). Then the process ''X<sub>t</sub>'' is a continuous martingale. Its martingale property follows immediately from the definitions, but its continuity is a very special fact – a special case of a general theorem stating that all Brownian martingales are continuous. A Brownian martingale is, by definition, a [[martingale (probability theory)|martingale]] adapted to the Brownian filtration; and the Brownian filtration is, by definition, the [[filtration (mathematics)|filtration]] generated by the Wiener process. | |||
=== Integrated Brownian motion === | |||
The time-integral of the Wiener process | |||
:<math>W^{(-1)}(t) := \int_0^t W(s) ds</math> | |||
is called '''integrated Brownian motion''' or '''integrated Wiener process'''. It arises in many applications and can be shown to have the distribution ''N''(0, ''t''<sup>3</sup>/3), calculus lead using the fact that the covariation of the Wiener process is <math> t \wedge s </math>.<ref>Forum, [http://wilmott.com/messageview.cfm?catid=4&threadid=39502 "Variance of integrated Wiener process"], 2009.</ref> | |||
=== Time change === | |||
Every continuous martingale (starting at the origin) is a time changed Wiener process. | |||
'''Example:''' 2''W''<sub>''t''</sub> = ''V''(4''t'') where ''V'' is another Wiener process (different from ''W'' but distributed like ''W''). | |||
'''Example.''' <math> W_t^2 - t = V_{A(t)} </math> where <math> A(t) = 4 \int_0^t W_s^2 \, \mathrm{d} s </math> and ''V'' is another Wiener process. | |||
In general, if ''M'' is a continuous martingale then <math> M_t - M_0 = V_{A(t)} </math> where ''A''(''t'') is the [[quadratic variation]] of ''M'' on [0, ''t''], and ''V'' is a Wiener process. | |||
'''Corollary.''' (See also [[Doob's martingale convergence theorems]]) Let ''M<sub>t</sub>'' be a continuous martingale, and | |||
:<math>M^-_\infty = \liminf_{t\to\infty} M_t,</math> | |||
:<math>M^+_\infty = \limsup_{t\to\infty} M_t. </math> | |||
Then only the following two cases are possible: | |||
: <math> -\infty < M^-_\infty = M^+_\infty < +\infty,</math> | |||
:<math>-\infty = M^-_\infty < M^+_\infty = +\infty; </math> | |||
other cases (such as <math> M^-_\infty = M^+_\infty = +\infty, </math> <math> M^-_\infty < M^+_\infty < +\infty </math> etc.) are of probability 0. | |||
Especially, a nonnegative continuous martingale has a finite limit (as ''t'' → ∞) almost surely. | |||
All stated (in this subsection) for martingales holds also for [[local martingale]]s. | |||
===Change of measure=== | |||
A wide class of [[Semimartingale#Continuous semimartingales|continuous semimartingales]] (especially, of [[diffusion process]]es) is related to the Wiener process via a combination of time change and [[Girsanov theorem|change of measure]]. | |||
Using this fact, the [[Wiener process#Qualitative properties|qualitative properties]] stated above for the Wiener process can be generalized to a wide class of continuous semimartingales.<ref>Revuz, D., & Yor, M. (1999). Continuous martingales and Brownian motion (Vol. 293). Springer.</ref> <ref>Doob, J. L. (1953). Stochastic processes (Vol. 101). Wiley: New York.</ref> | |||
=== Complex-valued Wiener process === | |||
The complex-valued Wiener process may be defined as a complex-valued random process of the form ''Z<sub>t</sub>'' = ''X<sub>t</sub>'' + ''iY<sub>t</sub>'' where ''X<sub>t</sub>'', ''Y<sub>t</sub>'' are independent Wiener processes (real-valued).<ref>{{Citation|title = Estimation of Improper Complex-Valued Random Signals in Colored Noise by Using the Hilbert Space Theory|url = http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/login.jsp?url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fiel5%2F18%2F4957623%2F04957648.pdf%3Farnumber%3D4957648&authDecision=-203 | journal = IEEE Transactions on Information Theory | pages = 2859–2867 | volume = 55 | issue = 6 | doi = 10.1109/TIT.2009.2018329 | last1 = Navarro-moreno | first1 = J. | |||
| last2 = Estudillo-martinez | first2 = M.D | last3 = Fernandez-alcala | first3 = R.M. | last4 = Ruiz-molina | first4 = J.C. | accessdate = 2010-03-30}}</ref> | |||
==== Self-similarity ==== | |||
Brownian scaling, time reversal, time inversion: the same as in the real-valued case. | |||
Rotation invariance: for every complex number ''c'' such that |''c''| = 1 the process ''cZ<sub>t</sub>'' is another complex-valued Wiener process. | |||
==== Time change ==== | |||
If ''f'' is an [[entire function]] then the process <math> f(Z_t)-f(0) </math> is a time-changed complex-valued Wiener process. | |||
'''Example:''' <math> Z_t^2 = (X_t^2-Y_t^2) + 2 X_t Y_t i = U_{A(t)} </math> where | |||
:<math>A(t) = 4 \int_0^t |Z_s|^2 \, \mathrm{d} s </math> | |||
and ''U'' is another complex-valued Wiener process. | |||
In contrast to the real-valued case, a complex-valued martingale is generally not a time-changed complex-valued Wiener process. For example, the martingale 2''X<sub>t</sub>'' + ''iY<sub>t</sub>'' is not (here ''X<sub>t</sub>'', ''Y<sub>t</sub>'' are independent Wiener processes, as before). | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[Abstract Wiener space]] | |||
* [[Classical Wiener space]] | |||
* [[Chernoff's distribution]] | |||
==Notes== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
{{More footnotes|date=February 2010}} | |||
==References== | |||
* [[Hagen Kleinert|Kleinert, Hagen]], ''Path Integrals in Quantum Mechanics, Statistics, Polymer Physics, and Financial Markets'', 4th edition, World Scientific (Singapore, 2004); Paperback ISBN 981-238-107-4 '' (also available online: [http://www.physik.fu-berlin.de/~kleinert/b5 PDF-files])'' | |||
* Stark,Henry, [[Woods, John|John W. Woods]], ''Probability and Random Processes with Applications to Signal Processing'', 3rd edition, Prentice Hall (New Jersey, 2002); Textbook ISBN 0-13-020071-9 | |||
* [[Rick Durrett|Durrett, R.]] (2000) ''Probability: theory and examples'',4th edition. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-76539-0 | |||
* Daniel Revuz and Marc Yor, ''Continuous martingales and Brownian motion'', second edition, Springer-Verlag 1994. | |||
==External links== | |||
*[http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/109N/more_stuff/Applets/brownian/applet.html Brownian motion java simulation] | |||
*[http://xxx.imsc.res.in/abs/physics/0412132 Article for the school-going child] | |||
*[http://arxiv.org/abs/0705.1951 Brownian Motion, "Diverse and Undulating"] | |||
*[http://physerver.hamilton.edu/Research/Brownian/index.html Discusses history, botany and physics of Brown's original observations, with videos] | |||
*[http://www.gizmag.com/einsteins-prediction-finally-witnessed/16212/ "Einstein's prediction finally witnessed one century later"] : a test to observe the velocity of Brownian motion | |||
{{Stochastic processes}} | |||
[[Category:Stochastic processes]] | |||
[[Category:Martingale theory]] | |||
[[Category:Variants of random walks]] | |||
Revision as of 03:39, 4 February 2014
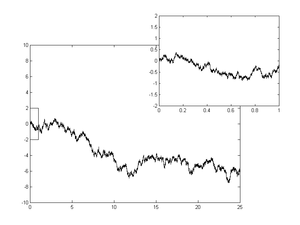

In mathematics, the Wiener process is a continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of Norbert Wiener. It is often called standard Brownian motion, after Robert Brown. It is one of the best known Lévy processes (càdlàg stochastic processes with stationary independent increments) and occurs frequently in pure and applied mathematics, economics, quantitative finance and physics.
The Wiener process plays an important role both in pure and applied mathematics. In pure mathematics, the Wiener process gave rise to the study of continuous time martingales. It is a key process in terms of which more complicated stochastic processes can be described. As such, it plays a vital role in stochastic calculus, diffusion processes and even potential theory. It is the driving process of Schramm–Loewner evolution. In applied mathematics, the Wiener process is used to represent the integral of a Gaussian white noise process, and so is useful as a model of noise in electronics engineering, instrument errors in filtering theory and unknown forces in control theory.
The Wiener process has applications throughout the mathematical sciences. In physics it is used to study Brownian motion, the diffusion of minute particles suspended in fluid, and other types of diffusion via the Fokker–Planck and Langevin equations. It also forms the basis for the rigorous path integral formulation of quantum mechanics (by the Feynman–Kac formula, a solution to the Schrödinger equation can be represented in terms of the Wiener process) and the study of eternal inflation in physical cosmology. It is also prominent in the mathematical theory of finance, in particular the Black–Scholes option pricing model.
Characterizations of the Wiener process
The Wiener process Wt is characterized by three properties:[1]
- W0 = 0
- The function t → Wt is almost surely everywhere continuous
- Wt has independent increments with Wt−Ws ~ N(0, t−s) (for 0 ≤ s < t), where N(μ, σ2) denotes the normal distribution with expected value μ and variance σ2.
The last condition means that if 0 ≤ s1 < t1 ≤ s2 < t2 then Wt1−Ws1 and Wt2−Ws2 are independent random variables, and the similar condition holds for n increments.
An alternative characterization of the Wiener process is the so-called Lévy characterization that says that the Wiener process is an almost surely continuous martingale with W0 = 0 and quadratic variation [Wt, Wt] = t (which means that Wt2−t is also a martingale).
A third characterization is that the Wiener process has a spectral representation as a sine series whose coefficients are independent N(0, 1) random variables. This representation can be obtained using the Karhunen–Loève theorem.
Another characterization of a Wiener process is the Definite integral (from zero to time t) of a zero mean, unit variance, delta correlated ("white") Gaussian process.
The Wiener process can be constructed as the scaling limit of a random walk, or other discrete-time stochastic processes with stationary independent increments. This is known as Donsker's theorem. Like the random walk, the Wiener process is recurrent in one or two dimensions (meaning that it returns almost surely to any fixed neighborhood of the origin infinitely often) whereas it is not recurrent in dimensions three and higherPotter or Ceramic Artist Truman Bedell from Rexton, has interests which include ceramics, best property developers in singapore developers in singapore and scrabble. Was especially enthused after visiting Alejandro de Humboldt National Park.. Unlike the random walk, it is scale invariant, meaning that
is a Wiener process for any nonzero constant α. The Wiener measure is the probability law on the space of continuous functions g, with g(0) = 0, induced by the Wiener process. An integral based on Wiener measure may be called a Wiener integral.
Properties of a one-dimensional Wiener process
Basic properties
The unconditional probability density function at a fixed time t:
The expectation is zero:
The variance, using the computational formula, is t:
The covariance and correlation:
The results for the expectation and variance follow immediately from the definition that increments have a normal distribution, centered at zero. Thus
The results for the covariance and correlation follow from the definition that non-overlapping increments are independent, of which only the property that they are uncorrelated is used. Suppose that t1 < t2.
Substituting
we arrive at:
Since W(t1) = W(t1)−W(t0) and W(t2)−W(t1), are independent,
Thus
Wiener representation
Wiener (1923) also gave a representation of a Brownian path in terms of a random Fourier series. If are independent Gaussian variables with mean zero and variance one, then
and
represent a Brownian motion on . The scaled process
is a Brownian motion on (cf. Karhunen–Loève theorem).
Running maximum
The joint distribution of the running maximum
and Wt is
To get the unconditional distribution of , integrate over −∞ < w ≤ m :
And the expectation[2]
Self-similarity

Brownian scaling
For every c > 0 the process is another Wiener process.
Time reversal
The process for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1 is distributed like Wt for 0 ≤ t ≤ 1.
Time inversion
The process is another Wiener process.
A class of Brownian martingales
If a polynomial p(x, t) satisfies the PDE
then the stochastic process
is a martingale.
Example: is a martingale, which shows that the quadratic variation of W on [0, t] is equal to t. It follows that the expected time of first exit of W from (−c, c) is equal to c2.
More generally, for every polynomial p(x, t) the following stochastic process is a martingale:
where a is the polynomial
is a martingale, which shows that the quadratic variation of the martingale on [0, t] is equal to
About functions p(xa, t) more general than polynomials, see local martingales.
Some properties of sample paths
The set of all functions w with these properties is of full Wiener measure. That is, a path (sample function) of the Wiener process has all these properties almost surely.
Qualitative properties
- For every ε > 0, the function w takes both (strictly) positive and (strictly) negative values on (0, ε).
- The function w is continuous everywhere but differentiable nowhere (like the Weierstrass function).
- Points of local maximum of the function w are a dense countable set; the maximum values are pairwise different; each local maximum is sharp in the following sense: if w has a local maximum at t then
- The function w has no points of local increase, that is, no t > 0 satisfies the following for some ε in (0, t): first, w(s) ≤ w(t) for all s in (t − ε, t), and second, w(s) ≥ w(t) for all s in (t, t + ε). (Local increase is a weaker condition than that w is increasing on (t − ε, t + ε).) The same holds for local decrease.
- The function w is of unbounded variation on every interval.
- Zeros of the function w are a nowhere dense perfect set of Lebesgue measure 0 and Hausdorff dimension 1/2 (therefore, uncountable).
Quantitative properties
Law of the iterated logarithm
Modulus of continuity
Local modulus of continuity:
Global modulus of continuity (Lévy):
Local time
The image of the Lebesgue measure on [0, t] under the map w (the pushforward measure) has a density Lt(·). Thus,
for a wide class of functions f (namely: all continuous functions; all locally integrable functions; all non-negative measurable functions). The density Lt is (more exactly, can and will be chosen to be) continuous. The number Lt(x) is called the local time at x of w on [0, t]. It is strictly positive for all x of the interval (a, b) where a and b are the least and the greatest value of w on [0, t], respectively. (For x outside this interval the local time evidently vanishes.) Treated as a function of two variables x and t, the local time is still continuous. Treated as a function of t (while x is fixed), the local time is a singular function corresponding to a nonatomic measure on the set of zeros of w.
These continuity properties are fairly non-trivial. Consider that the local time can also be defined (as the density of the pushforward measure) for a smooth function. Then, however, the density is discontinuous, unless the given function is monotone. In other words, there is a conflict between good behavior of a function and good behavior of its local time. In this sense, the continuity of the local time of the Wiener process is another manifestation of non-smoothness of the trajectory.
Related processes

The stochastic process defined by
is called a Wiener process with drift μ and infinitesimal variance σ2. These processes exhaust continuous Lévy processes.
Two random processes on the time interval [0, 1] appear, roughly speaking, when conditioning the Wiener process to vanish on both ends of [0,1]. With no further conditioning, the process takes both positive and negative values on [0, 1] and is called Brownian bridge. Conditioned also to stay positive on (0, 1), the process is called Brownian excursion.[3] In both cases a rigorous treatment involves a limiting procedure, since the formula P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B)/P(B) does not apply when P(B) = 0.
A geometric Brownian motion can be written
It is a stochastic process which is used to model processes that can never take on negative values, such as the value of stocks.
The stochastic process
is distributed like the Ornstein–Uhlenbeck process.
The time of hitting a single point x > 0 by the Wiener process is a random variable with the Lévy distribution. The family of these random variables (indexed by all positive numbers x) is a left-continuous modification of a Lévy process. The right-continuous modification of this process is given by times of first exit from closed intervals [0, x].
The local time L = (Lxt)x ∈ R, t ≥ 0 of a Brownian motion describes the time that the process spends at the point x. Formally
where δ is the Dirac delta function. The behaviour of the local time is characterised by Ray–Knight theorems.
Brownian martingales
Let A be an event related to the Wiener process (more formally: a set, measurable with respect to the Wiener measure, in the space of functions), and Xt the conditional probability of A given the Wiener process on the time interval [0, t] (more formally: the Wiener measure of the set of trajectories whose concatenation with the given partial trajectory on [0, t] belongs to A). Then the process Xt is a continuous martingale. Its martingale property follows immediately from the definitions, but its continuity is a very special fact – a special case of a general theorem stating that all Brownian martingales are continuous. A Brownian martingale is, by definition, a martingale adapted to the Brownian filtration; and the Brownian filtration is, by definition, the filtration generated by the Wiener process.
Integrated Brownian motion
The time-integral of the Wiener process
is called integrated Brownian motion or integrated Wiener process. It arises in many applications and can be shown to have the distribution N(0, t3/3), calculus lead using the fact that the covariation of the Wiener process is .[4]
Time change
Every continuous martingale (starting at the origin) is a time changed Wiener process.
Example: 2Wt = V(4t) where V is another Wiener process (different from W but distributed like W).
Example. where and V is another Wiener process.
In general, if M is a continuous martingale then where A(t) is the quadratic variation of M on [0, t], and V is a Wiener process.
Corollary. (See also Doob's martingale convergence theorems) Let Mt be a continuous martingale, and
Then only the following two cases are possible:
other cases (such as etc.) are of probability 0.
Especially, a nonnegative continuous martingale has a finite limit (as t → ∞) almost surely.
All stated (in this subsection) for martingales holds also for local martingales.
Change of measure
A wide class of continuous semimartingales (especially, of diffusion processes) is related to the Wiener process via a combination of time change and change of measure.
Using this fact, the qualitative properties stated above for the Wiener process can be generalized to a wide class of continuous semimartingales.[5] [6]
Complex-valued Wiener process
The complex-valued Wiener process may be defined as a complex-valued random process of the form Zt = Xt + iYt where Xt, Yt are independent Wiener processes (real-valued).[7]
Self-similarity
Brownian scaling, time reversal, time inversion: the same as in the real-valued case.
Rotation invariance: for every complex number c such that |c| = 1 the process cZt is another complex-valued Wiener process.
Time change
If f is an entire function then the process is a time-changed complex-valued Wiener process.
and U is another complex-valued Wiener process.
In contrast to the real-valued case, a complex-valued martingale is generally not a time-changed complex-valued Wiener process. For example, the martingale 2Xt + iYt is not (here Xt, Yt are independent Wiener processes, as before).
See also
Notes
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
References
- Kleinert, Hagen, Path Integrals in Quantum Mechanics, Statistics, Polymer Physics, and Financial Markets, 4th edition, World Scientific (Singapore, 2004); Paperback ISBN 981-238-107-4 (also available online: PDF-files)
- Stark,Henry, John W. Woods, Probability and Random Processes with Applications to Signal Processing, 3rd edition, Prentice Hall (New Jersey, 2002); Textbook ISBN 0-13-020071-9
- Durrett, R. (2000) Probability: theory and examples,4th edition. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-76539-0
- Daniel Revuz and Marc Yor, Continuous martingales and Brownian motion, second edition, Springer-Verlag 1994.
External links
- Brownian motion java simulation
- Article for the school-going child
- Brownian Motion, "Diverse and Undulating"
- Discusses history, botany and physics of Brown's original observations, with videos
- "Einstein's prediction finally witnessed one century later" : a test to observe the velocity of Brownian motion
- ↑ Durrett 1996, Sect. 7.1
- ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ One of the biggest reasons investing in a Singapore new launch is an effective things is as a result of it is doable to be lent massive quantities of money at very low interest rates that you should utilize to purchase it. Then, if property values continue to go up, then you'll get a really high return on funding (ROI). Simply make sure you purchase one of the higher properties, reminiscent of the ones at Fernvale the Riverbank or any Singapore landed property Get Earnings by means of Renting
In its statement, the singapore property listing - website link, government claimed that the majority citizens buying their first residence won't be hurt by the new measures. Some concessions can even be prolonged to chose teams of consumers, similar to married couples with a minimum of one Singaporean partner who are purchasing their second property so long as they intend to promote their first residential property. Lower the LTV limit on housing loans granted by monetary establishments regulated by MAS from 70% to 60% for property purchasers who are individuals with a number of outstanding housing loans on the time of the brand new housing purchase. Singapore Property Measures - 30 August 2010 The most popular seek for the number of bedrooms in Singapore is 4, followed by 2 and three. Lush Acres EC @ Sengkang
Discover out more about real estate funding in the area, together with info on international funding incentives and property possession. Many Singaporeans have been investing in property across the causeway in recent years, attracted by comparatively low prices. However, those who need to exit their investments quickly are likely to face significant challenges when trying to sell their property – and could finally be stuck with a property they can't sell. Career improvement programmes, in-house valuation, auctions and administrative help, venture advertising and marketing, skilled talks and traisning are continuously planned for the sales associates to help them obtain better outcomes for his or her shoppers while at Knight Frank Singapore. No change Present Rules
Extending the tax exemption would help. The exemption, which may be as a lot as $2 million per family, covers individuals who negotiate a principal reduction on their existing mortgage, sell their house short (i.e., for lower than the excellent loans), or take part in a foreclosure course of. An extension of theexemption would seem like a common-sense means to assist stabilize the housing market, but the political turmoil around the fiscal-cliff negotiations means widespread sense could not win out. Home Minority Chief Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) believes that the mortgage relief provision will be on the table during the grand-cut price talks, in response to communications director Nadeam Elshami. Buying or promoting of blue mild bulbs is unlawful.
A vendor's stamp duty has been launched on industrial property for the primary time, at rates ranging from 5 per cent to 15 per cent. The Authorities might be trying to reassure the market that they aren't in opposition to foreigners and PRs investing in Singapore's property market. They imposed these measures because of extenuating components available in the market." The sale of new dual-key EC models will even be restricted to multi-generational households only. The models have two separate entrances, permitting grandparents, for example, to dwell separately. The vendor's stamp obligation takes effect right this moment and applies to industrial property and plots which might be offered inside three years of the date of buy. JLL named Best Performing Property Brand for second year running
The data offered is for normal info purposes only and isn't supposed to be personalised investment or monetary advice. Motley Fool Singapore contributor Stanley Lim would not personal shares in any corporations talked about. Singapore private home costs increased by 1.eight% within the fourth quarter of 2012, up from 0.6% within the earlier quarter. Resale prices of government-built HDB residences which are usually bought by Singaporeans, elevated by 2.5%, quarter on quarter, the quickest acquire in five quarters. And industrial property, prices are actually double the levels of three years ago. No withholding tax in the event you sell your property. All your local information regarding vital HDB policies, condominium launches, land growth, commercial property and more
There are various methods to go about discovering the precise property. Some local newspapers (together with the Straits Instances ) have categorised property sections and many local property brokers have websites. Now there are some specifics to consider when buying a 'new launch' rental. Intended use of the unit Every sale begins with 10 p.c low cost for finish of season sale; changes to 20 % discount storewide; follows by additional reduction of fiftyand ends with last discount of 70 % or extra. Typically there is even a warehouse sale or transferring out sale with huge mark-down of costs for stock clearance. Deborah Regulation from Expat Realtor shares her property market update, plus prime rental residences and houses at the moment available to lease Esparina EC @ Sengkang - ↑ Forum, "Variance of integrated Wiener process", 2009.
- ↑ Revuz, D., & Yor, M. (1999). Continuous martingales and Brownian motion (Vol. 293). Springer.
- ↑ Doob, J. L. (1953). Stochastic processes (Vol. 101). Wiley: New York.
- ↑ Many property agents need to declare for the PIC grant in Singapore. However, not all of them know find out how to do the correct process for getting this PIC scheme from the IRAS. There are a number of steps that you need to do before your software can be approved.
Naturally, you will have to pay a safety deposit and that is usually one month rent for annually of the settlement. That is the place your good religion deposit will likely be taken into account and will kind part or all of your security deposit. Anticipate to have a proportionate amount deducted out of your deposit if something is discovered to be damaged if you move out. It's best to you'll want to test the inventory drawn up by the owner, which can detail all objects in the property and their condition. If you happen to fail to notice any harm not already mentioned within the inventory before transferring in, you danger having to pay for it yourself.
In case you are in search of an actual estate or Singapore property agent on-line, you simply should belief your intuition. It's because you do not know which agent is nice and which agent will not be. Carry out research on several brokers by looking out the internet. As soon as if you end up positive that a selected agent is dependable and reliable, you can choose to utilize his partnerise in finding you a home in Singapore. Most of the time, a property agent is taken into account to be good if he or she locations the contact data on his website. This may mean that the agent does not mind you calling them and asking them any questions relating to new properties in singapore in Singapore. After chatting with them you too can see them in their office after taking an appointment.
Have handed an trade examination i.e Widespread Examination for House Brokers (CEHA) or Actual Property Agency (REA) examination, or equal; Exclusive brokers are extra keen to share listing information thus making certain the widest doable coverage inside the real estate community via Multiple Listings and Networking. Accepting a severe provide is simpler since your agent is totally conscious of all advertising activity related with your property. This reduces your having to check with a number of agents for some other offers. Price control is easily achieved. Paint work in good restore-discuss with your Property Marketing consultant if main works are still to be done. Softening in residential property prices proceed, led by 2.8 per cent decline within the index for Remainder of Central Region
Once you place down the one per cent choice price to carry down a non-public property, it's important to accept its situation as it is whenever you move in – faulty air-con, choked rest room and all. Get round this by asking your agent to incorporate a ultimate inspection clause within the possibility-to-buy letter. HDB flat patrons routinely take pleasure in this security net. "There's a ultimate inspection of the property two days before the completion of all HDB transactions. If the air-con is defective, you can request the seller to repair it," says Kelvin.
15.6.1 As the agent is an intermediary, generally, as soon as the principal and third party are introduced right into a contractual relationship, the agent drops out of the image, subject to any problems with remuneration or indemnification that he could have against the principal, and extra exceptionally, against the third occasion. Generally, agents are entitled to be indemnified for all liabilities reasonably incurred within the execution of the brokers´ authority.
To achieve the very best outcomes, you must be always updated on market situations, including past transaction information and reliable projections. You could review and examine comparable homes that are currently available in the market, especially these which have been sold or not bought up to now six months. You'll be able to see a pattern of such report by clicking here It's essential to defend yourself in opposition to unscrupulous patrons. They are often very skilled in using highly unethical and manipulative techniques to try and lure you into a lure. That you must also protect your self, your loved ones, and personal belongings as you'll be serving many strangers in your home. Sign a listing itemizing of all of the objects provided by the proprietor, together with their situation. HSR Prime Recruiter 2010


![{\displaystyle E[W_{t}]=0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8b1ba46ce18f203f1dfd7a1e2701f4cb938dfb5d)
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {Var} (W_{t})=E\left[W_{t}^{2}\right]-E^{2}[W_{t}]=E\left[W_{t}^{2}\right]-0=E\left[W_{t}^{2}\right]=t.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cb3510130f603bd2f48b5530c06f4cde8ca25250)



![{\displaystyle \operatorname {cov} (W_{t_{1}},W_{t_{2}})=E\left[(W_{t_{1}}-E[W_{t_{1}}])\cdot (W_{t_{2}}-E[W_{t_{2}}])\right]=E\left[W_{t_{1}}\cdot W_{t_{2}}\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7bb1e24cf4729a0c507913914bc01a7628729270)

![{\displaystyle E[W_{t_{1}}\cdot W_{t_{2}}]=E\left[W_{t_{1}}\cdot ((W_{t_{2}}-W_{t_{1}})+W_{t_{1}})\right]=E\left[W_{t_{1}}\cdot (W_{t_{2}}-W_{t_{1}})\right]+E\left[W_{t_{1}}^{2}\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/64e7f8bfb8bbeb1555830ffeb5852429da2e2ea0)
![{\displaystyle E\left[W_{t_{1}}\cdot (W_{t_{2}}-W_{t_{1}})\right]=E[W_{t_{1}}]\cdot E[W_{t_{2}}-W_{t_{1}}]=0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e489fb1afaea9f6c1b0c240efabcf26ccae58f27)
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {cov} (W_{t_{1}},W_{t_{2}})=E\left[W_{t_{1}}^{2}\right]=t_{1}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1f6a44839369e2bb1ed68b25a6f53608dd8e4002)



![{\displaystyle [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/738f7d23bb2d9642bab520020873cccbef49768d)

![{\displaystyle [0,c]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d8f04abeab39818aa786f2e5f9cdf163379e60c6)




![{\displaystyle E[M_{t}]=\int _{0}^{\infty }mf_{M_{t}}(m)\,dm=\int _{0}^{\infty }m{\sqrt {\frac {2}{\pi t}}}e^{-{\frac {m^{2}}{2t}}}\,dm={\sqrt {\frac {2t}{\pi }}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c04813dbc8c7dfaf914e9bb35d6b4720c91d2fc9)


































